
Modbus, IEC 60870-5-103, IEC 60870-5-104, and IEC 61850 are widely used communication protocols in the fields of power systems and industrial automation. They exhibit significant differences in design objectives, architecture, data models, and application scenarios. Below is a detailed comparative analysis of them.
1. Protocol Overview
Modbus
Standard Type: General industrial control protocol (non-IEC, originally developed by Modicon).
Design Objective: Simplicity and openness for basic data exchange between devices (e.g., PLCs, sensors).
Application: Industrial automation, building automation, simple data acquisition (e.g., temperature, pressure sensors).
IEC 60870-5-103
Standard Type: IEC standard (specific to protection equipment).
Design Objective: Communication between protection relays and monitoring systems (e.g., fault recording, setting management).
Application: Microprocessor-based protection devices communicating with local monitoring systems (e.g., uploading protection trip signals).
IEC 60870-5-104
Standard Type: IEC standard (networked extension of 103).
Design Objective: Remote monitoring in power systems via TCP/IP (e.g., control center-to-substation communication).
Application: SCADA systems, wide-area dispatch automation (e.g., “Four Tele” functions: telemetry, telesignaling, telecontrol, and teleadjustment).
IEC 61850
Standard Type: IEC standard (core standard for smart grids).
Design Objective: High real-time performance, interoperability, and object-oriented data modeling for substation automation (SA).
Application: Smart substations (e.g., IED communication, GOOSE tripping, SV sampled values transmission).
2.Protocol Architecture & Communication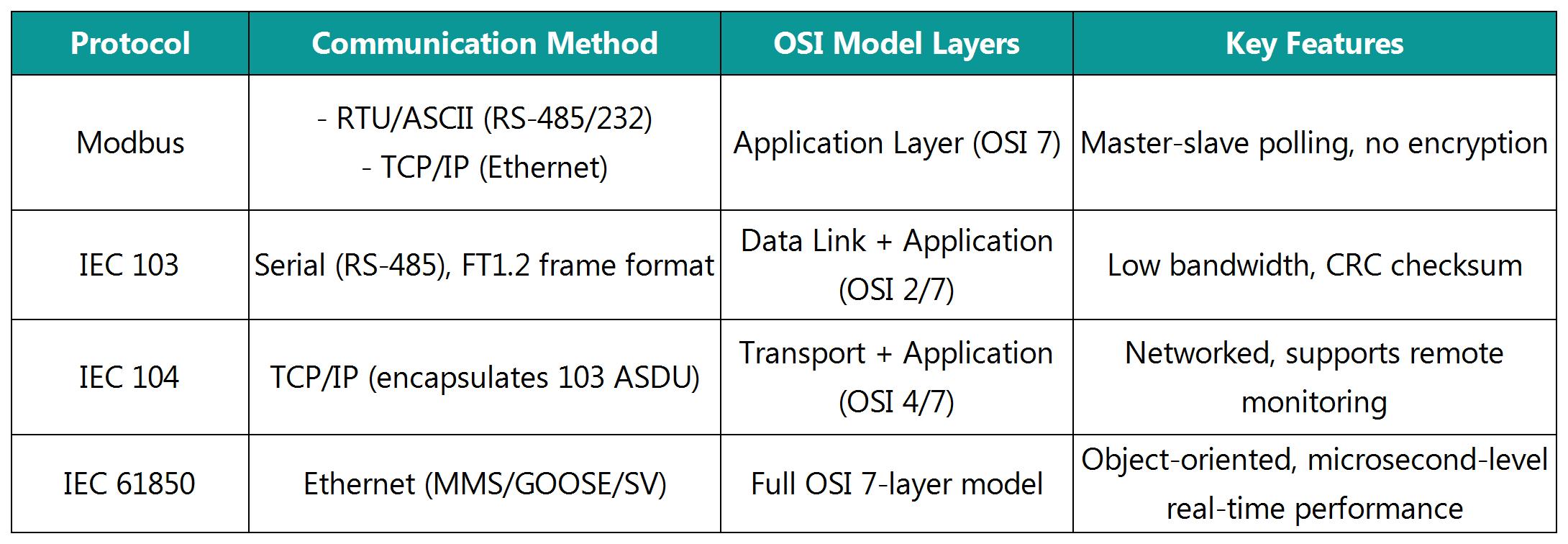
3. Core Functions & Features
Modbus
Functionality: Basic read/write (registers, coils).
Real-Time Performance: Low (master-slave polling introduces latency).
Security: No encryption or authentication.
Scalability: Poor (requires predefined address mapping).
IEC 103
Functionality: Protection-specific (fault recording, event logging, setting management).
Real-Time Performance: Medium (serial communication ≤19.2 kbps).
Reliability: Frame checksum (CRC), timeout retransmission.
Scalability: Limited (relies on predefined ASDU types).
IEC 104
Functionality: Extends 103 with “Four Tele” support.
Real-Time Performance: Better than 103 (TCP/IP reduces latency).
Reliability: TCP ensures data integrity but is affected by network jitter.
Application: Remote substation monitoring by control centers.
IEC 61850
Functionality:
MMS (Manufacturing Message Specification): Standard monitoring data.
GOOSE (Generic Object-Oriented Substation Event): Microsecond-level tripping signals.
SV (Sampled Values): Synchronized sampled data (e.g., merging units).
Real-Time Performance: Extremely high (GOOSE uses Layer 2 multicast).
Interoperability: Vendor-independent implementation.
Scalability: High (supports SCL configuration, plug-and-play).
4.Data Model Comparison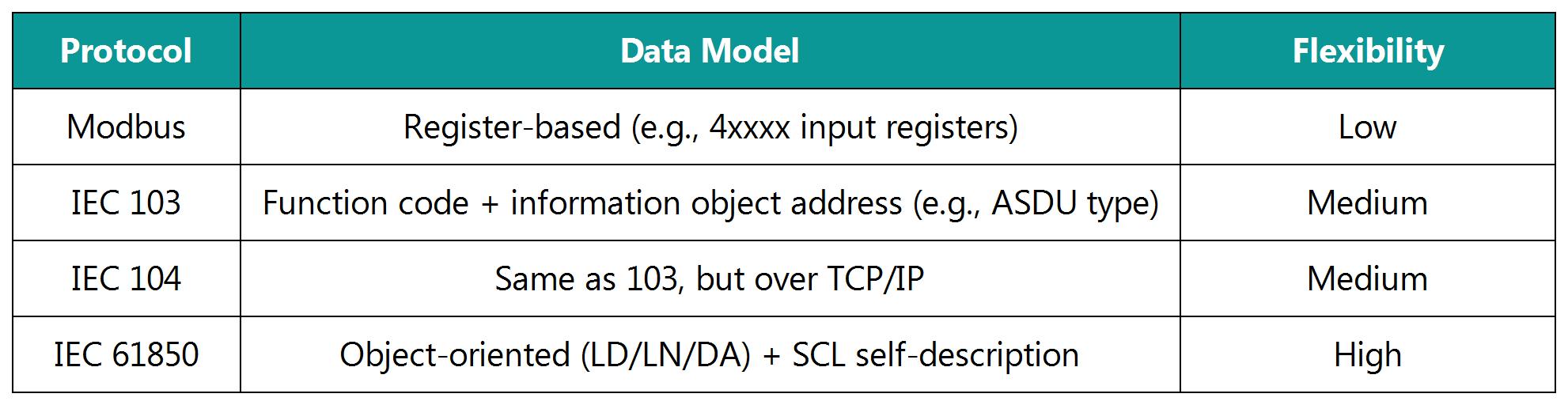
5. Typical Applications
Modbus: Turbine temperature monitoring, industrial sensor data collection.
IEC 103: Protection relay-to-local monitoring (e.g., fault records).
IEC 104: Remote substation control by SCADA systems.
IEC 61850: Fast tripping (GOOSE) in smart substations, renewable energy plant communication.
6. Future Trends
IEC 61850 is gradually replacing legacy protocols (e.g., 103/104) due to its flexibility and interoperability, especially in smart grids and renewables.
Hybrid Systems: Common deployments include:
IEC 61850 at station level, IEC 104 for control center communication, and Modbus for device-level data acquisition.
Protocol gateways (e.g., 104-to-61850) for integrating heterogeneous systems.
Summary
Modbus: Simple, low-cost, suitable for basic industrial control.
IEC 103: Protection-specific, serial communication.
IEC 104: Networked 103, ideal for remote monitoring.
IEC 61850: Core standard for smart substations, enabling high real-time performance and interoperability.
For deeper technical details (e.g., ASDU structure, GOOSE mechanisms), refer to IEC standards or industry documentation.








