
Generator differential protection is one of the most critical primary protections in generator relaying systems. Its core function is to rapidly and reliably clear internal short-circuit faults in generators, preventing severe equipment damag
I. Functions of Generator Differential Protection
1. Rapid Clearance of Internal Short-Circuit Faults
Protected Objects: Phase-to-phase faults, turn-to-turn faults (detectable by some differential schemes), and terminal connection faults in the stator winding.
Operating Speed: Typically trips within 20–40 ms (milliseconds), significantly faster than overcurrent protection (seconds).
Importance:
Short-circuit currents can reach 5–10 times the rated current. Failure to clear them quickly may lead to:
Insulation burnout → Generator failure
Localized core overheating and melting → Extremely high repair costs
Hydrogen explosions (in hydrogen-cooled generators)
2. Discrimination Between Internal and External Faults
Selective Protection: Operates only for faults within the protected zone, avoiding maloperation during external faults (e.g., grid or busbar faults).
Implementation:
Compares the vector difference between neutral-side current (IN) and terminal-side current (IT).
Under normal conditions, IN=IT, and the differential current Idiff =|IN−IT∣≈0.
During internal faults, IN≠IT, and Idiff exceeds the setting threshold, triggering the protection.
3. Prevention of Fault Propagation in the Power System
If an internal generator fault is not cleared promptly, it may cause:
Grid voltage collapse (especially for large-capacity generators).
Overcurrent damage to adjacent equipment (e.g., main transformers, busbars).
Torsional vibration in the generator shaft (short-circuit torque impacts may damage turbine components).
4. Enhancement of Power System Reliability
As a primary protection, the fast operation of differential protection avoids delayed action by backup protections (e.g., overcurrent or negative-sequence protection), minimizing outage impact.
II. Protection Scope of Generator Differential Protection
The protection scope is determined by the installation locations of current transformers (CTs) and typically includes the following:
1. Protected Zone (Internal Faults)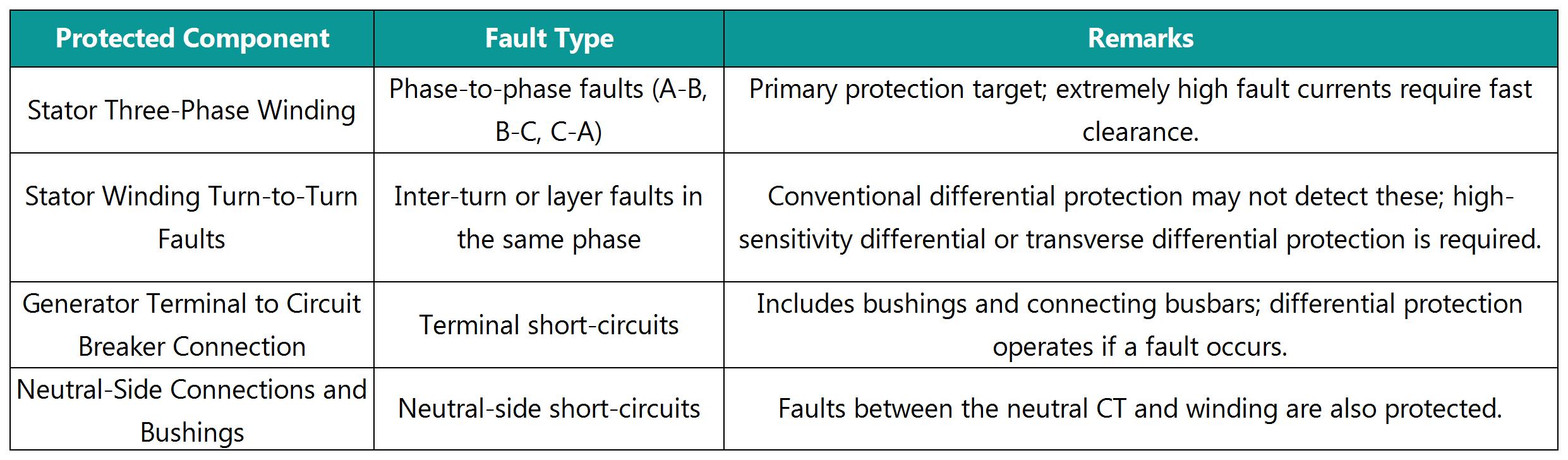
2. Non-Protected Zone (External Faults)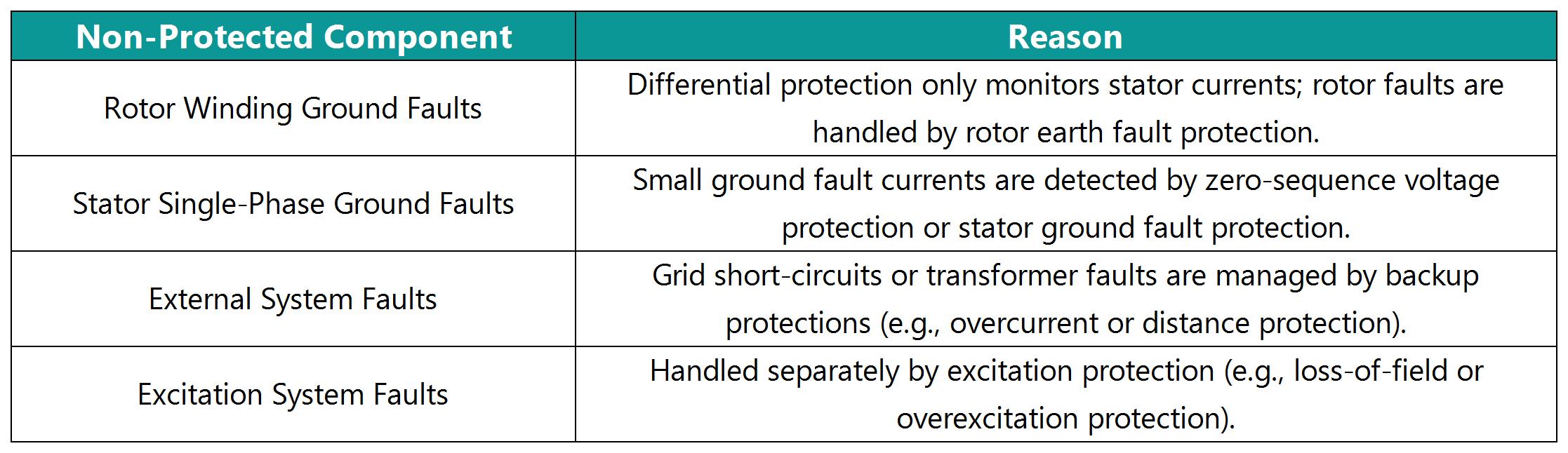
3. Determination of Protection Zone Boundaries
Key Factor: The protection zone is defined by CT installation locations.
Terminal CTs: Typically installed on the generator side of the circuit breaker.
Neutral CTs: Installed on the generator neutral connection.
Example:
If CTs are installed outside the generator breaker, the connection between the breaker and the grid is not protected by differential protection.
Incorrect neutral CT installation may prevent detection of neutral-side faults.








