Here is the professional English translation of the Industrial Plant Power Supply – Substation Solution, adhering to international standards (IEC/IEEE), accurate terminology, and correct grammar:
1. Power Consumption Scenario Overview
Typical Industrial Load Characteristics:
Equipment Types: High-power motors (e.g., compressors, pump sets), electric arc furnaces, variable frequency drives (VFDs), lighting systems, HVAC systems, automated production lines.
Operation Mode: 24/7 continuous production, peak load concentrated during daytime shifts.
Load Characteristics:
Impact Loads: Starting current of large motors reaches 6~8 times rated current (IEC 60034-12).
Non-linear Loads: Harmonics generated by VFDs/rectifiers (THDi up to 15%~30%, per IEEE 519).
Sensitive Equipment: PLCs, precision instruments require voltage fluctuation <±5% (IEC 61000-4-34).
Environmental Conditions: Class 3C3 (high temperature, dust, per IEC 60721-3-3).
2. Substation Capacity Calculation Analysis
Core Formulas (IEC 60364 / IEEE 141):
1. Total Calculated Load (kVA) = Demand Factor × Connected Load
2. Transformer Rating (kVA) = Total kVA / Diversity Factor
3. Short-Circuit Current Calculation: I_sc = U / (√3 × Z_s) (IEC 60909)
Calculation Steps:
1).Load Inventory (Example):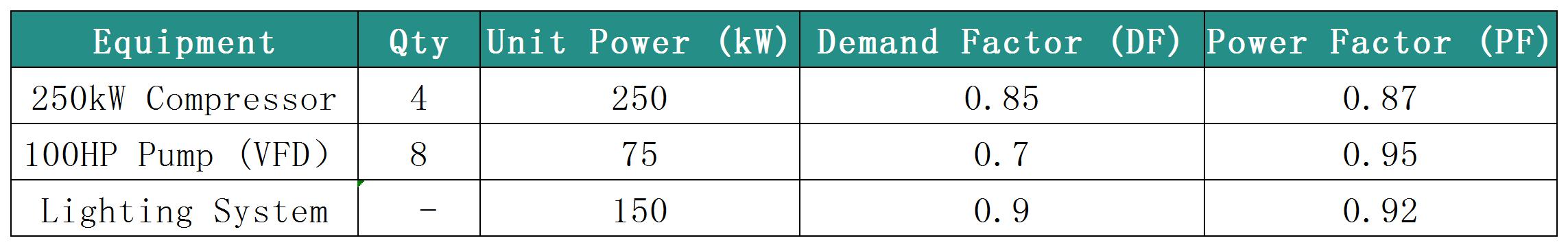 2).Active Power Calculation (kW):
2).Active Power Calculation (kW):
Compressors: 4 × 250kW × 0.85 = 850kW
Pumps: 8 × 75kW × 0.7 = 420kW
Lighting: 150kW × 0.9 = 135kW
Total P = 850 + 420 + 135 = 1405kW
3).Reactive Power Compensation (kVAR):
Target PF = 0.95 (IEEE 18)
Initial Q = P × tan(cos⁻¹(Initial PF))
Compensation Q_c = P × [tan(cos⁻¹(0.8)) – tan(cos⁻¹(0.95))]
4).Transformer Sizing (IEC 60076):
Total Apparent Power S = P / Target PF = 1405kW / 0.95 ≈ 1480kVA
Recommended Rating: 2×1000kVA (N+1 Redundancy)
5).Short-Circuit Current Analysis:
Assume 33kV Side SCC = 25kA (IEC 62271)
Transformer Impedance Z = 6% → LV Side I_sc ≈ 35kA
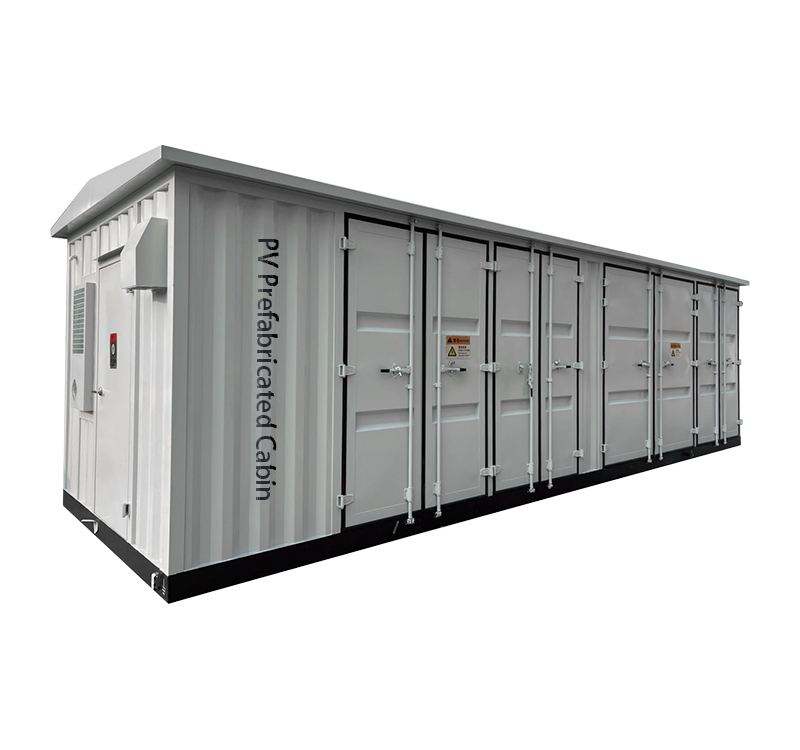
3. Substation Configuration
Primary System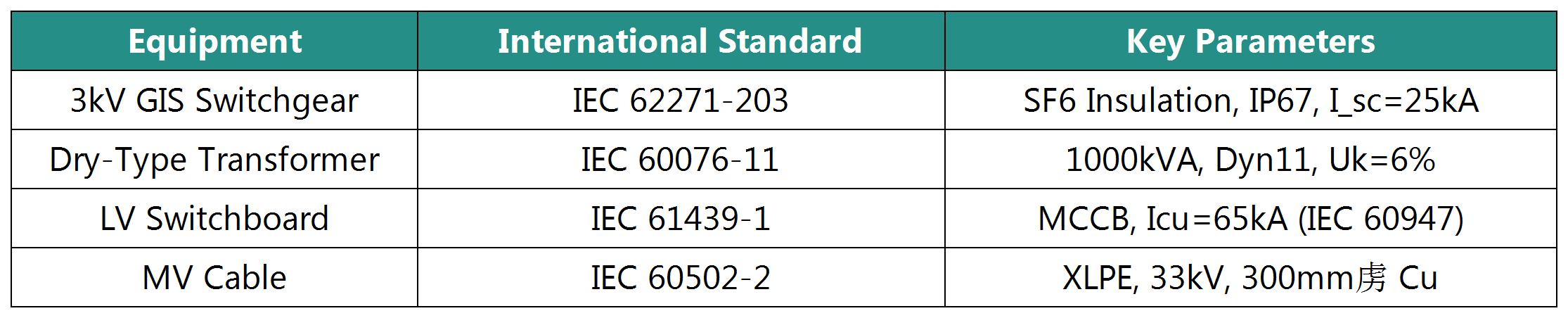
Secondary System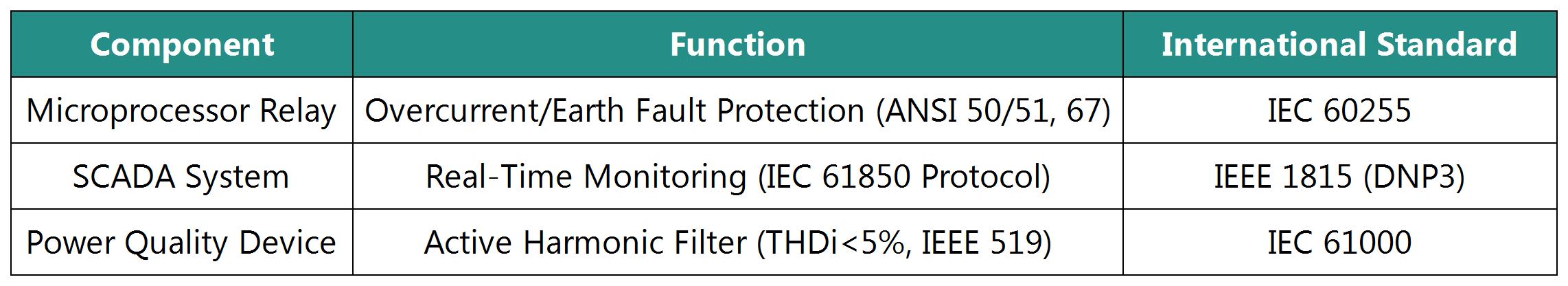
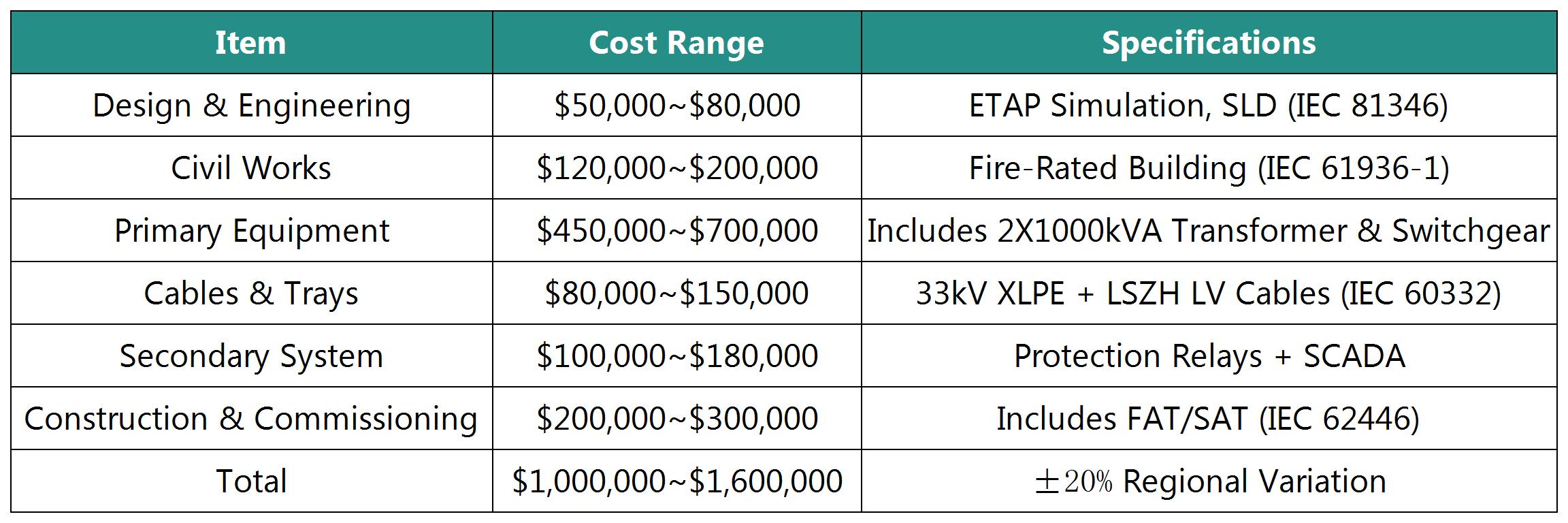
4. Cost Estimation (USD)
Based on North America/Europe Project Benchmarks (2024)