
1. Purpose of Voltage Rate-of-Change Blocking
Voltage rate-of-change blocking (dv/dt blocking) is primarily used to:
Prevent protection misoperation: Blocks associated protections (e.g., undervoltage or overvoltage protection) during rapid voltage fluctuations (e.g., short-circuit faults, capacitor switching, transformer inrush currents) to avoid false tripping caused by transient disturbances.
Enhance protection reliability: Distinguishes between actual faults and transient events, ensuring protective devices operate only when necessary.
Improve system stability: Reduces unnecessary protection trips, preventing cascading failures or load loss.
2. Key Functions of Voltage Rate-of-Change Blocking
The core functions include:
Real-time monitoring of voltage change rate (dv/dt): Calculates the instantaneous rate of voltage magnitude change (units: kV/s or %/s).
Blocking logic decision: Activates blocking when the voltage change rate exceeds a preset threshold.
Automatic recovery: Restores normal protection functionality once voltage stabilizes.
Typical Applications:
Voltage dips during initial short-circuit faults (prevents undervoltage protection misoperation).
Voltage fluctuations during capacitor bank switching or transformer energization.
Transient overvoltages caused by system oscillations or lightning strikes.
3. Working Principle of Voltage Rate-of-Change Blocking
The blocking logic operates through the following steps:
Signal Acquisition:
Measures three-phase voltage magnitudes (typically using positive-sequence or phase voltages).
Change Rate Calculation:
Computes the instantaneous voltage change rate:
dV/dt = (V t −V t−Δt)/Δt
where V t = current voltage, Δt = sampling interval.
Threshold Comparison:
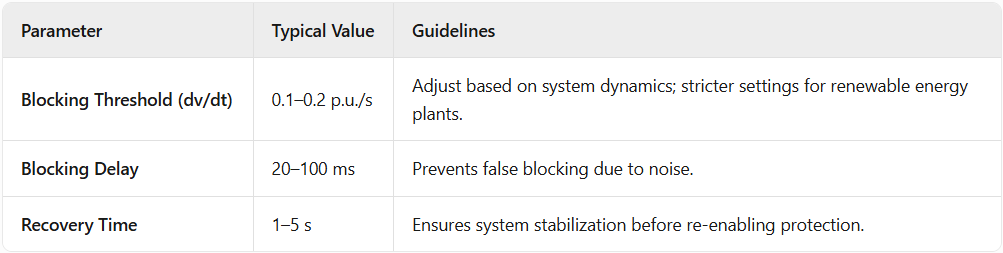
If ∣dV/dt∣ exceeds the setting (e.g., 0.1–0.2 p.u./s), the system identifies an abnormal transient and triggers blocking.
Protection Blocking:
Blocks affected protection functions (e.g., undervoltage protection) and logs the event.
Recovery Mechanism:
Automatically releases the blocking after the voltage change rate remains below the threshold for a set duration (e.g., 1–5 seconds).
4.Voltage Rate-of-Change Blocking Key Parameters and Setting Recommendations
5.Conclusion
Voltage rate-of-change blocking is a critical logic in power system protection, identifying transient disturbances by monitoring dv/dt and intelligently blocking protection to prevent misoperation. It is essential for short-circuit events, capacitor switching, and other transient scenarios. Optimal performance requires careful threshold and delay settings to balance sensitivity and reliability.








