
Parallel operation involves connecting two or more independent AC power sources (e.g., generators, grids) to share electrical loads seamlessly. This process—synchronization—demands precise matching of voltage magnitude, frequency, and phase angles between systems before interconnection. Critical for grid expansion, backup power, and renewable integration, it enables redundant supply during failures. Failure to synchronize correctly risks catastrophic equipment damage due to out-of-phase currents. Modern systems use auto-synchronizers for real-time adjustments, allowing generators to support grids without interruption. Parallel operation underpins reliable large-scale power networks but requires rigorous protocols like IEEE 1547 compliance.
1. Parallel operation :Definition & Fundamentals
Parallel operation synchronizes independent AC systems (generators/grids) to operate as a unified network. Core requirements include:
2. Parallel operation:Synchronization Process
3. Parallel operation:Key Applications
4. Parallel operation:Risks & Safety Protocols
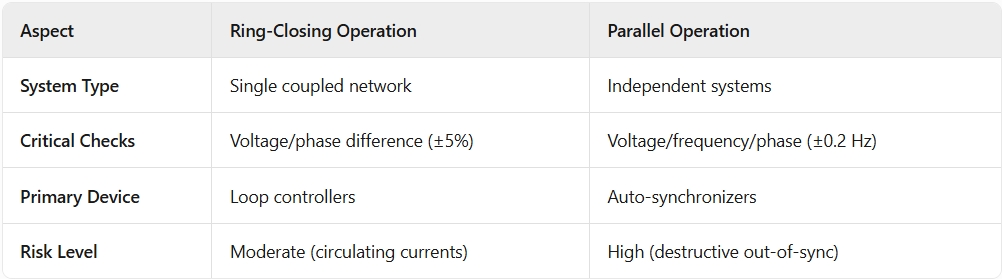
5. Comparison: Ring-Closing vs. Parallel Operation
6.Parallel operation: Industry Standards
7. Case Study: Grid Resilience
During California’s 2020 blackouts, parallel operation enabled rapid back-feeding from Nevada’s grid via








