
1. What is Arc Flash?
An arc flash is a violent electrical explosion resulting from a fault in an electrical system. It releases immense amounts of radiant and thermal energy, posing severe risks to personnel and equipment. Effective Arc Flash Protection is essential to manage this hazard.
2. How Does an Arc Flash Relay Work?
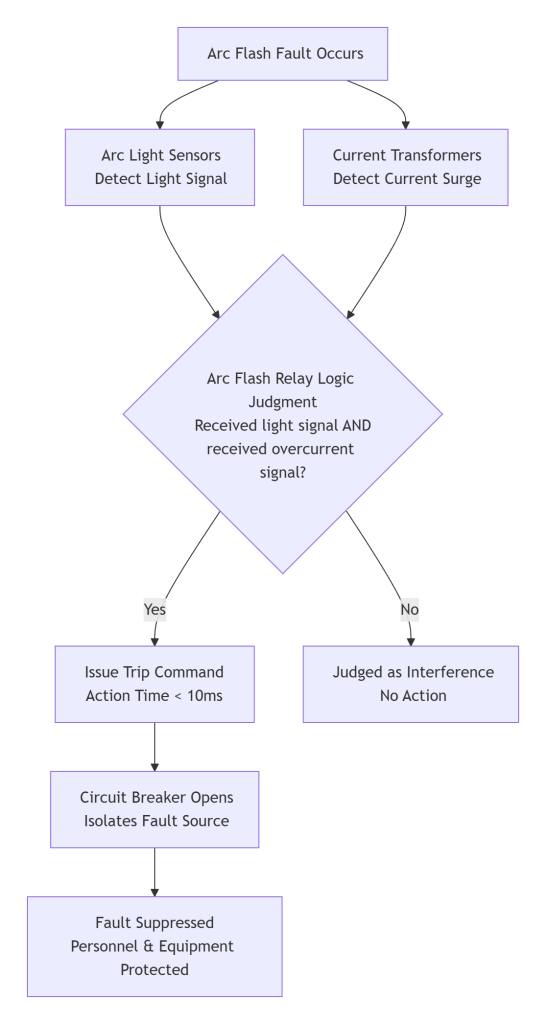
The core of an Arc Flash Protection system is the Arc Flash Protection Relay (or main unit). It operates on a dual criteria principle: it must simultaneously receive a light signal from an arc flash sensor and a current surge signal from a current transformer. This logic ensures both speed and reliability, preventing false trips.
Path A: Light Detection – Specialized Arc Light Sensors detect the specific wavelength of the intense light emitted by the arc flash almost instantaneously.
Path B: Current Detection – Current Transformers (CTs) detect the sudden surge in current that accompanies the fault.
3. Key Components of an Arc Flash Protection System
A complete Arc Flash Protection system consists of three main parts: the central Arc Flash Relay for processing commands, light sensors that act as the system’s “eyes” to detect the specific light signature of a flash, and current sensors to provide the necessary confirming fault signal.
Yes (Both Conditions Met): The Arc Flash Relay confirms a genuine arc flash event and immediately issues a Trip Command to the circuit breaker in an extremely short time, typically less than 10 milliseconds.
No (Condition Not Met): If only one signal is present (e.g., light from a camera flash or current surge from a motor start), the relay Judges it as Interference and takes No Action, preventing a false trip.
4. The Critical Importance of Arc Flash Protection
Implementing robust Arc Flash Protection is a cornerstone of modern Electrical Safety. Its unparalleled speed is the only way to sufficiently reduce the incident energy of an arc flash event, directly saving lives and avoiding costly equipment destruction and downtime.
5. Applications for Arc Flash Relays
Arc Flash Protection systems are vital anywhere electrical risk is high. They are widely installed in medium and low-voltage switchgear across industries like oil and gas, data centers, manufacturing plants, and utilities, where they form the last line of defense for Electrical Safety.








