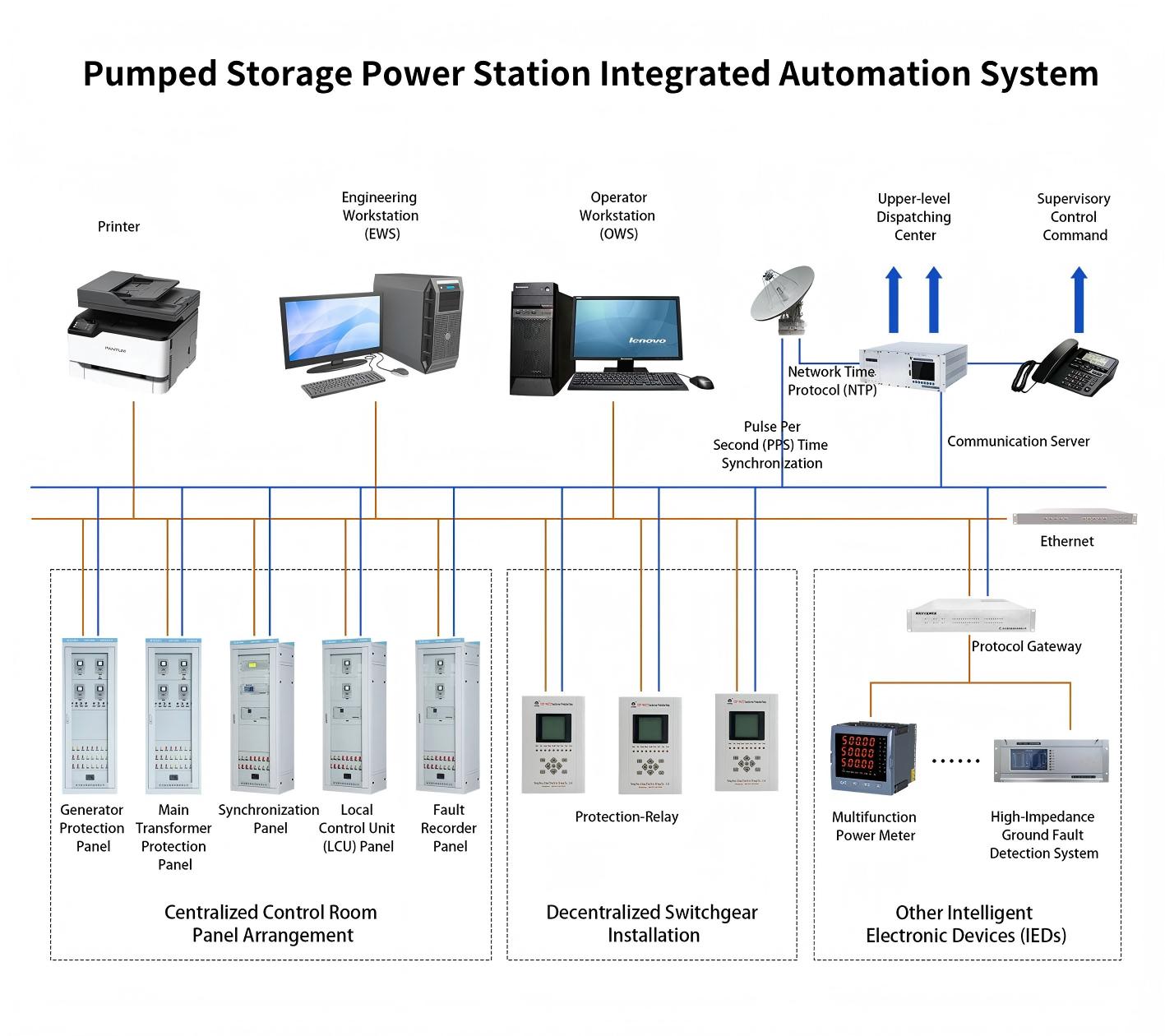
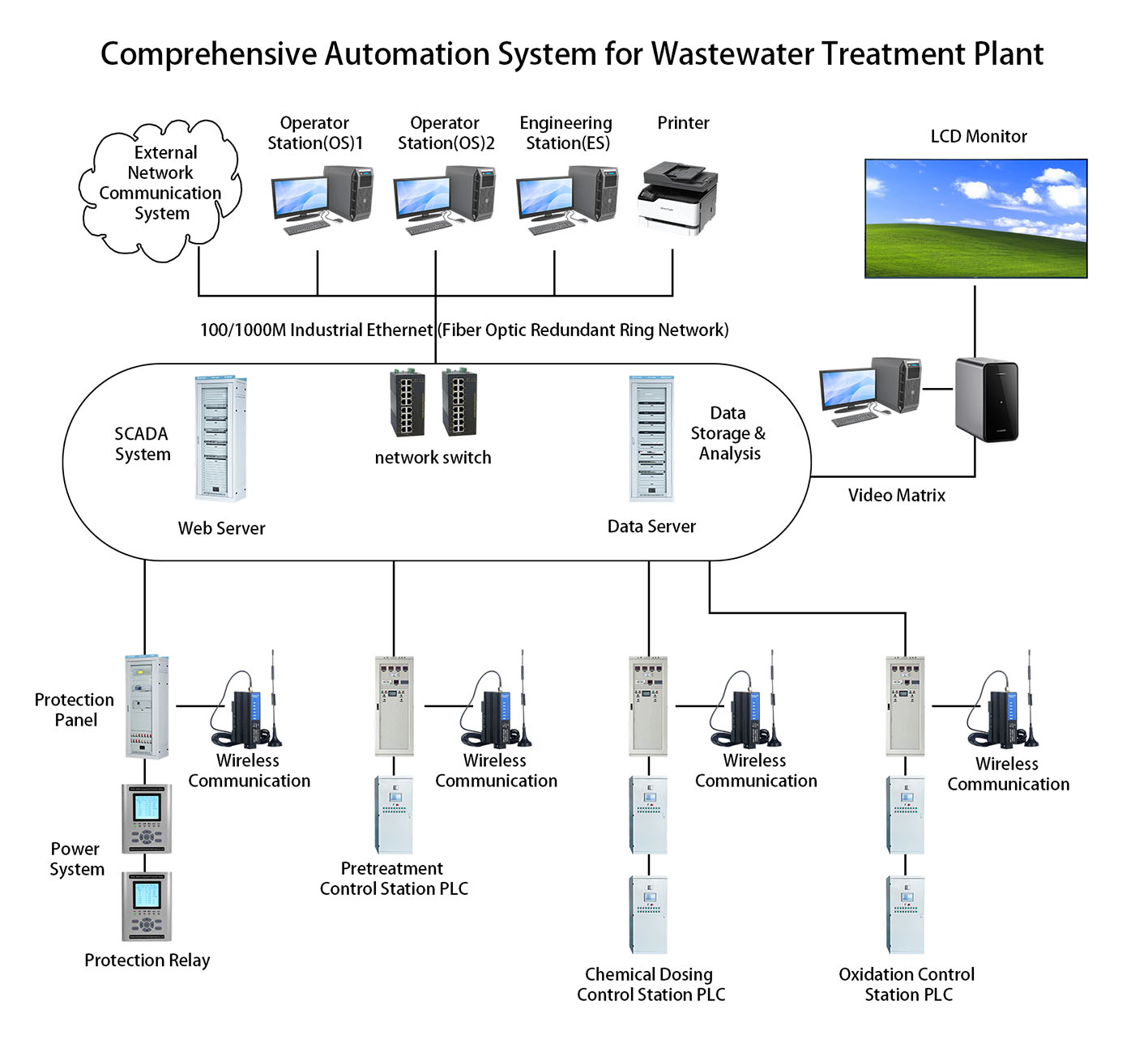
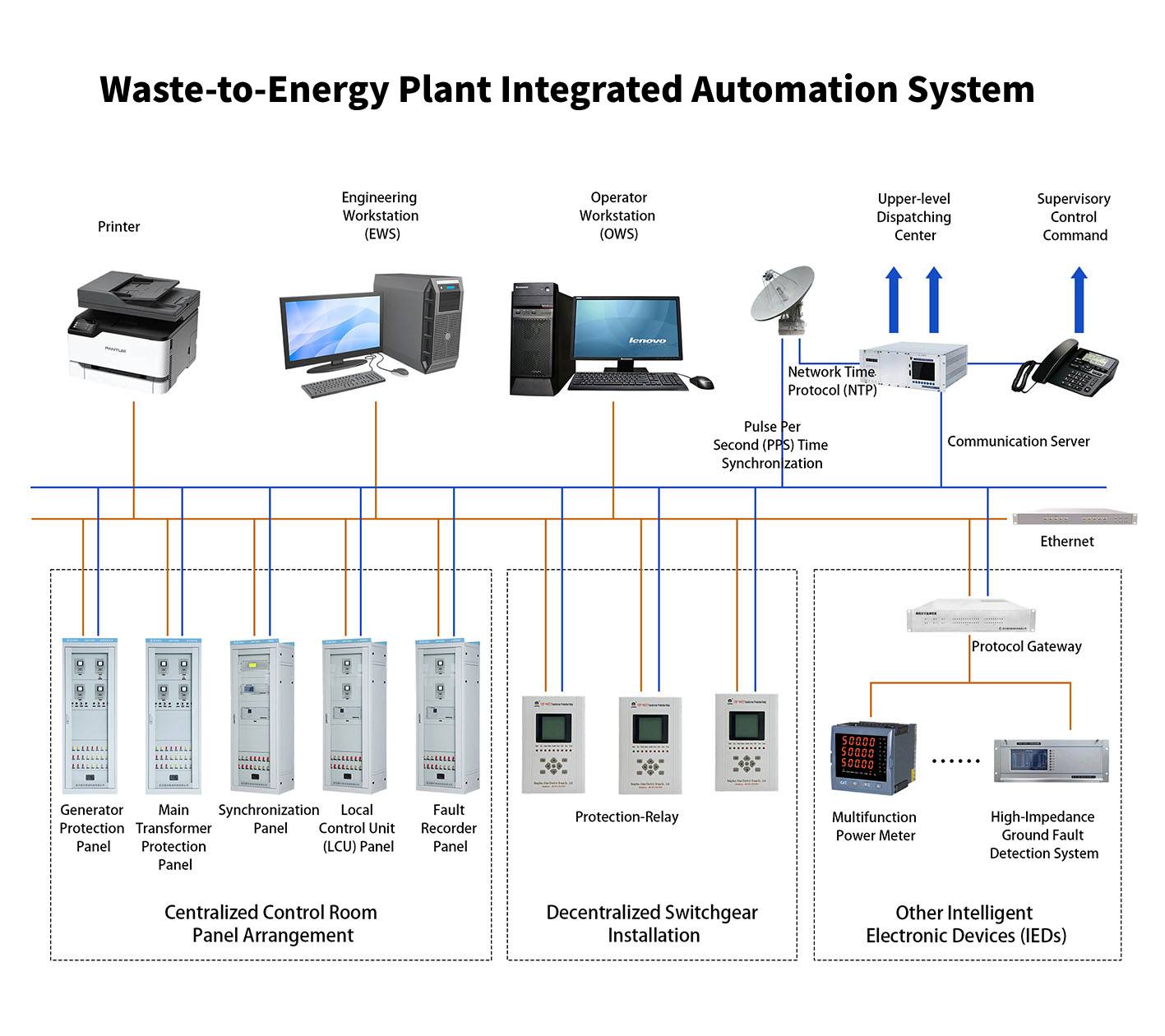
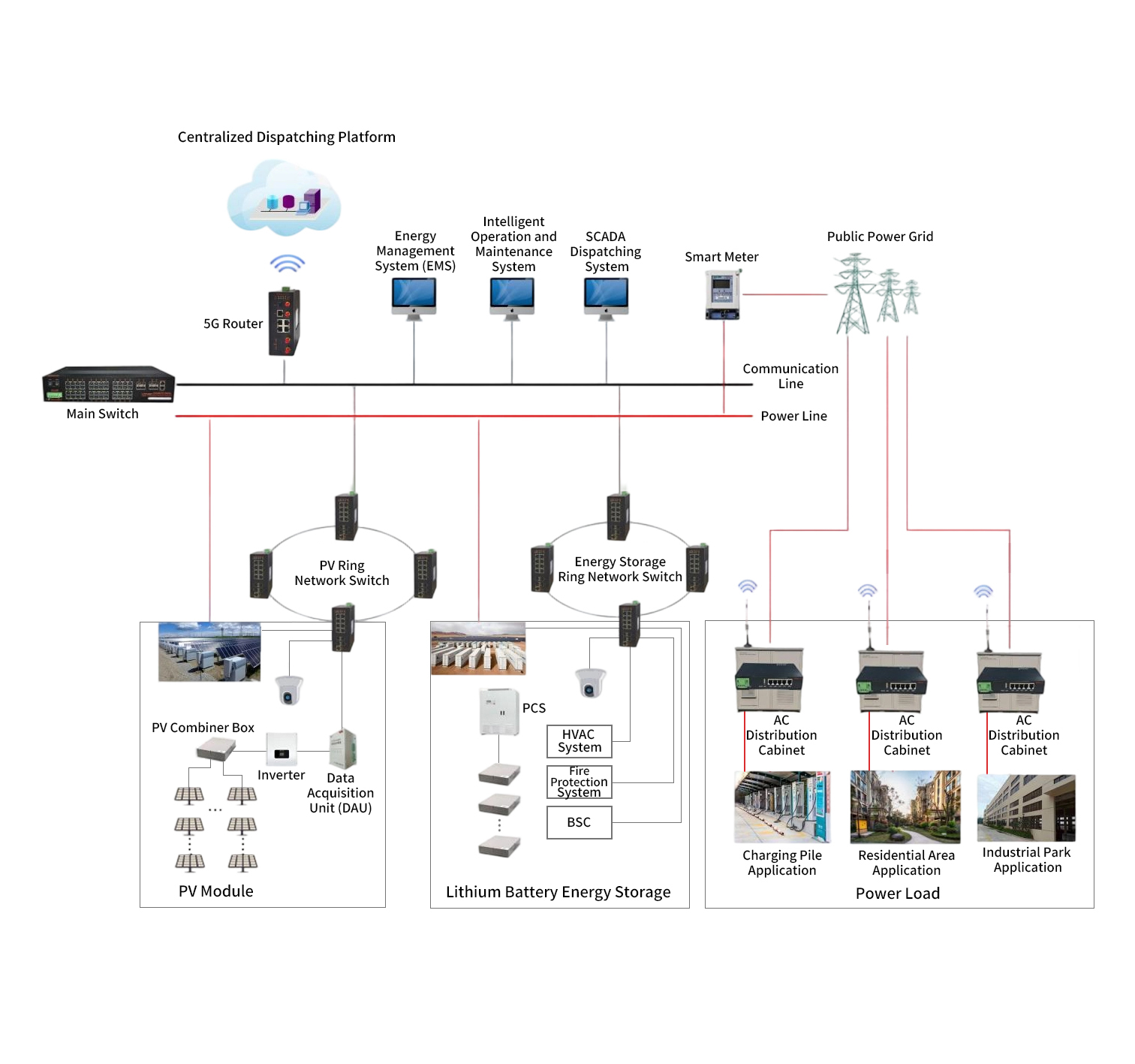
1. System Overview
The Fire Power Plant Integrated Automation System is an integrated platform centered on computer control technology, combining process control, electrical monitoring, protection systems, and information management. Its core objectives are:
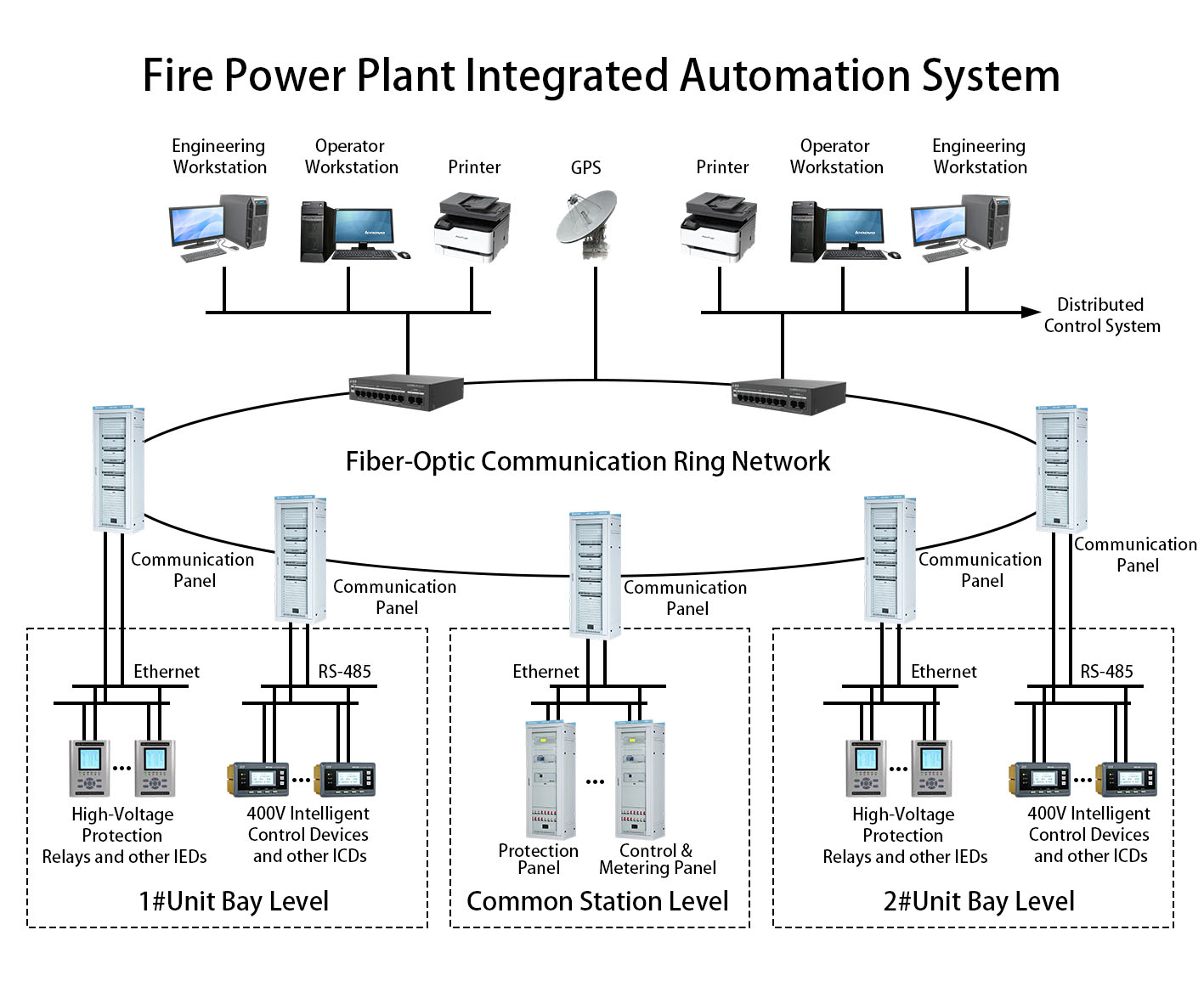
Safety and Reliability: Enabling automatic regulation under all operating conditions and rapid fault isolation.
Economic Operation: Optimizing fuel, steam, and power production processes to reduce coal consumption.
Environmental Compliance: Real-time monitoring of emission parameters (SO₂, NOₓ, particulate matter).
Reduced Manned Operation: Minimizing reliance on field operations through centralized monitoring.
The system adopts a Hierarchical Distributed Architecture:
Process Control Layer: Directly interfaces with boilers, turbines, generators, and auxiliary equipment.
Supervisory Layer: Centralized data acquisition and human-machine interface (HMI).
Management Layer: Production data analysis and decision support.
2. System Composition and Subsystem Functions
(1) Distributed Control System (DCS)
Primary Function: Core control of main processes (boiler, turbine, auxiliary systems).
Key Hardware Functions:
Controller (Processing Unit): Executes control algorithms to regulate valves, fans, and actuators in real time.
I/O Modules: Acquire signals from sensors (temperature/pressure/flow) and output control commands.
Redundant Network: Dual-ring topology ensures zero-interruption communication.
(2) Electrical Control System (ECS)
Primary Function: Intelligent monitoring and switching of high/low-voltage auxiliary power supplies.
Key Hardware Functions:
Microprocessor-Based Protection & Control Devices: Provide overcurrent, ground fault protection, and power metering for feeders/motors.
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): Enables seamless backup power source transition during faults.
(3) Substation Control System (NCS)
Primary Function: Remote operation of 132kV/66kV switchyards.
Key Hardware Functions:
Line Protection Relays: Differential and distance protection to ensure grid security.
Phasor Measurement Unit (PMU): Monitors grid stability in real time.
(4) Auxiliary Process Control System (PLC + SCADA)
Primary Function: Centralized monitoring of coal handling, water treatment, and ash handling.
Key Hardware Functions:
PLC Controller: Executes sequential logic control (e.g., conveyor start/stop sequences).
Industrial HMI: Local operation and status visualization.
(5) Fire Alarm System (FAS)
Primary Function: Fire protection for critical areas (cable tunnels, oil storage).
Key Hardware Functions:
Heat/Smoke Detectors: Early fire hazard identification.
Fire Control Panel: Automatically activates sprinklers/smoke extraction systems.
(6) Plant Information System (PIS/SIS)
Primary Function: Plant-wide data analysis and performance optimization.
Key Hardware Functions:
Real-Time Database Server: Stores high-resolution historical data.
Computational Engine: Performs coal consumption analysis and load dispatch optimization.
3. Hardware/Software Configuration and Functions
(1) Computer Monitoring System
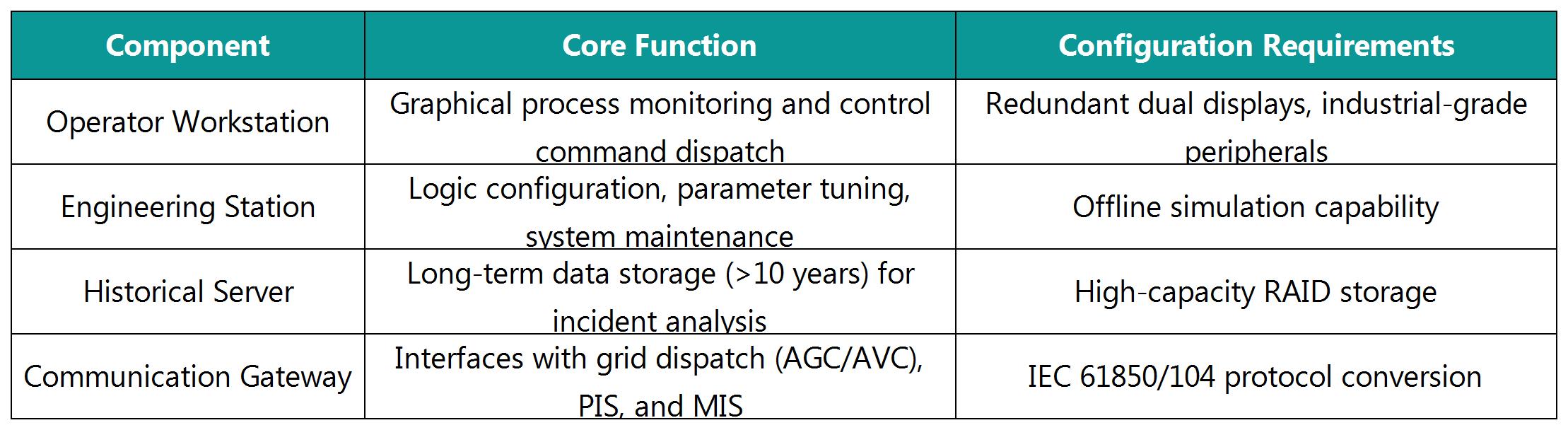 (2) Protection & Automation Equipment
(2) Protection & Automation Equipment
Relay Protection Systems:
Generator Protection: Stator ground fault, loss-of-field protection.
Transformer Protection: Differential protection, Buchholz relay for internal faults.
Auxiliary System Protection: Instantaneous overcurrent, overload protection.
System Automation:
Fault Recorder: Captures pre/post-fault electrical waveforms.
Synchronizer: Automatically adjusts phase/angle during grid synchronization.
(3) Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) & Remote Terminal Units (RTU)
PLC: Implements sequential control and interlocking logic in auxiliary systems.
RTU: Monitors remote areas (e.g., ash dykes) via fiber/wireless communication.
(4) Key Software Functions
SCADA Software: Dynamic process graphics, alarm prioritization, trend analysis.
Advanced Applications:
Automatic Generation Control (AGC): Responds to grid load commands.
Intelligent Soot Blowing Optimization: Reduces steam loss based on fouling models.
Cybersecurity: Firewalls and encryption for network attack mitigation.
Core Design Principles
Redundancy: 1:1 redundancy for controllers, networks, and power supplies.
Open Architecture: Supports OPC UA, Modbus TCP, and other standard interfaces.
Scalability: 20% spare I/O capacity and cabinet space provision.
Network Security: Segregation into Security Zones I/II/III with intrusion detection.
This solution achieves integrated monitoring, control, and management for modern fire power plants, meeting requirements for efficiency, cleanliness, and intelligent operation.