

Applicable Scope :Applicable Scope: Designed for 11kV & 33kV power systems (default per model code ’98’). Supports generator-grid synchronization with voltage range 60-120% Un, frequency range ±10% Fn, and phase angle tolerance ±5°. Operating temperature -25°C to +70°C.
Product functions(ANSI):25 | 25/79 | 27/79 | 39/50BF
Communication functions :Supported Protocols : IEC 60870-5-103 (over Ethernet) | MODBUS RTU (via RS-485) | IEC 61850 (Ed.2 or Ed.1, as applicable)
Interfaces:2× Ethernet Ports (IEEE 802.3 compliant, 10/100 Mbps) | 2× RS-485 Ports (ANSI/TIA-485-A standard, galvanically isolated)
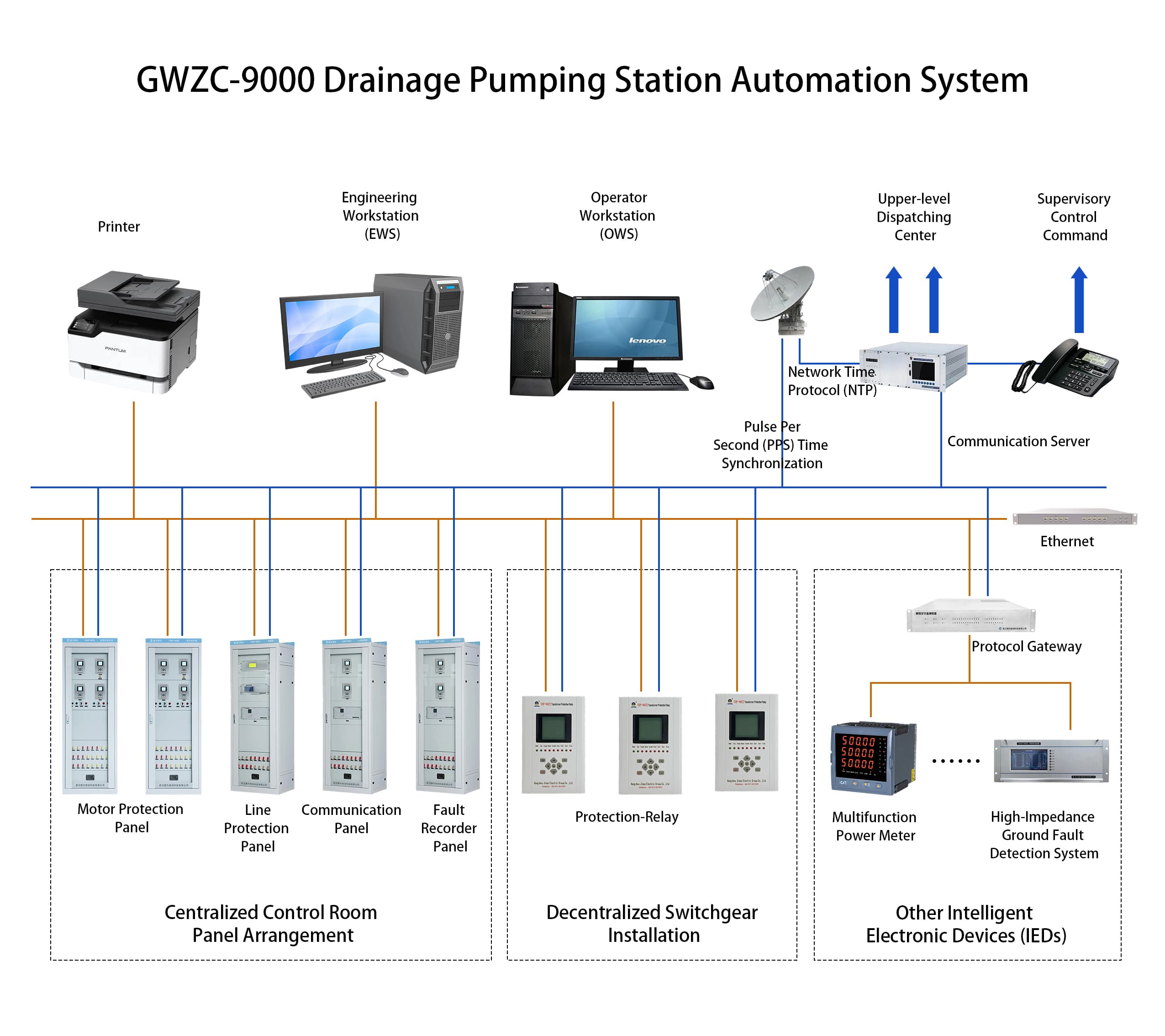
GWZC-9803 Automatic Synchronizing Device (ASD) Introduction
GWZC-9803 Automatic Synchronizing Device (ASD) ensures seamless generator-grid connection for high-voltage substations (33kV/66kV). Key features include microprocessor-based phase angle calculation, automatic voltage/frequency regulation assistance, and anti-reverse power protection. Equipped with dual communication interfaces and event recording for grid operation analysis.
GWZC-9803 Automatic Synchronizing Device (ASD) Functions and Characteristics
Primary Functions (ANSI Codes):
Communication Functions:
Key Characteristics:
GWZC-9803 Automatic Synchronizing Device (ASD) Working Principle
The GWZC-9803 ASD automatically synchronizes a generator or power source with a running bus (grid) to enable safe, smooth connection by ensuring key parameters meet predefined thresholds before closing the circuit breaker.
Core Synchronization Conditions
The device verifies three critical factors:
Working Process
Operation Modes
Electrical Specifications
Power Supply:
● AC: 85-264V, 47-63Hz (≤15% THD)
● DC: 100-370V (≤5% ripple)
Rated AC Parameters:
● Voltage: 100V/√3 or 100V
● Current: 5A/1A
● Frequency: 50Hz
Overload Capacity:
● Current Circuit: 2×In continuous | 10×In (10s) | 40×In (1s)
● Voltage Circuit: 1.5×Un continuous
Power Consumption:
● Supply: <10W (static), ≤15W (trip)
● Current Circuit: ≤1VA/phase (5A) / ≤0.5VA/phase (1A)
● Voltage Circuit: ≤0.5VA/phase
Digital Output:
● Dry contact (8A@250VAC / 30VDC)
● Dielectric: 4kVAC (coil-contact), 1kVAC (open contact)
● Operating Time: 5ms (typ) / 8ms (max)
● Mechanical Life: 100k operations
Protection Performance
Operating Range:
● Voltage: 0.5-120V (phase)
● Current: 0.02-20×In
● Zero-Seq Current: 0.05-20A
● Frequency: 35-65Hz | Delay: 0-100s
Accuracy:
● Voltage/Current: ±2.5% or ±0.1V/±0.05A (whichever greater)
● Frequency: ±0.01Hz
● Settings: ±2.5%
Trip Time:
● Instantaneous: ≤35ms (≥1.2× setting)
● Time-Delayed: ≤1% of setting or 35ms
Measurement & Monitoring
Range:
● Voltage: 0.5-120V | Current: 0.02-1.2×In
Accuracy:
● V/I: ±0.2% | Frequency: ±0.01Hz | Other: 0.5%
● Time Sync: ≤2ms | SOE: ≤1ms
Event Recording:
● 128 protection trips/operations
● 32 self-tests/fault waveforms (COMTRADE)
Environmental & Mechanical
Operating Temp:
● Standard: -10°C to +55°C
● Extended: -40°C to +70°C*
Storage Temp: -40°C to +80°C
Humidity: 5-90% RH (non-condensing)
Pressure: 60-110 kPa
Compliance:
● IEC 60255-21 (vibration/shock)
● IEC 61000-6 (EMC)










