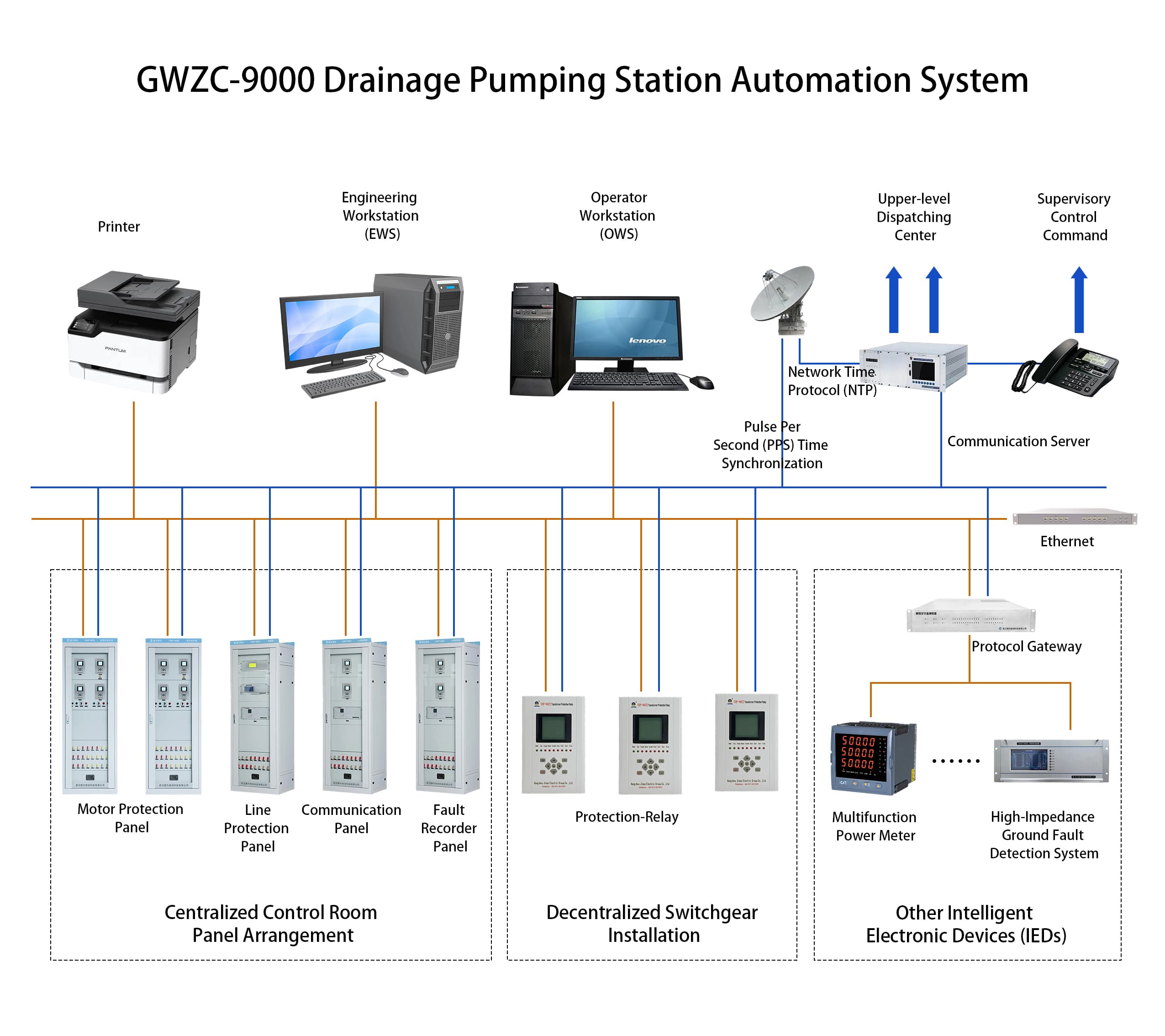
1. Comprehensive Protection Relay Definition
A comprehensive protection relay (or integrated protection relay) is a smart electrical device that combines multiple protection functions to monitor power systems (e.g., generators, transformers, motors, transmission lines) and quickly isolate faults to ensure safety. It features modular design and digital processing, allowing customizable protection logic via software.
2. Comprehensive Protection Relay Functions
- Multi-protection integration: Overcurrent, overvoltage, undervoltage, ground fault, differential protection, frequency protection, etc.
- Real-time monitoring: Measures voltage, current, frequency, and power, transmitting data via communication interfaces (e.g., RS485, Ethernet).
- Fault recording: Stores event logs, waveforms, and timestamps for post-failure analysis.
- Automation: Supports auto-reclosing, load switching, and other control functions.
3. Comprehensive Protection Relay Working Principle
- Signal acquisition: CTs (current transformers) and PTs (voltage transformers) convert analog signals to digital.
- Data processing: A microprocessor filters and analyzes signals (e.g., RMS calculation, harmonic analysis).
- Logic decision: Compares values with preset thresholds (e.g., overcurrent setting) and time curves (e.g., inverse-time characteristic).
- Action output: Triggers relay contacts or communication signals to trip the circuit breaker.
Example: In overcurrent protection, if current exceeds the threshold for a set duration, the relay sends a trip command.
4. Comprehensive Protection Relay Protection Targets
- Generators: Differential, loss-of-excitation, reverse power
- Transformers: Overload, Buchholz relay (gas detection)
- Motors: Locked rotor, phase imbalance
- Transmission Lines: Distance protection, earth fault (zero-sequence)
5. Comprehensive Protection Relay Activation Conditions
- Electrical anomalies: Overcurrent, overvoltage, frequency deviation, phase imbalance.
- Non-electrical anomalies: High transformer oil temperature (via sensors).
- Logic combinations: E.g., “overcurrent + low voltage” indicates a short circuit.
Key Settings:
- Threshold values: Trip levels (e.g., 120% rated current).
- Time delays: Prevents nuisance tripping (e.g., 0.5-second delay).
6.Protection Outcomes
Direct results:
- Tripping: Disconnects the faulty circuit (breaker opens).
- Alarm: Audible/visual alerts or SCADA notifications.
Indirect effects:
- System reconfiguration: Backup power activation (e.g., ATS).
- Fault isolation: Prevents cascading failures.
Special cases:
- Auto-reclosing: Restores power after transient faults (e.g., lightning strikes).
Conclusion
- Comprehensive protection relays act as ”smart guardians” for power systems, enhancing reliability through fast fault detection and isolation. Their effectiveness depends on accurate settings and coordination with other protective devices (e.g., selective tripping).