IEC standard switchgear and UL standard switchgear (represented by UL1558 and UL891) fall under different technical systems in power systems, with differences mainly reflected in their standard frameworks, structural design, performance requirements, and applicable scenarios. The following is a comprehensive comparative analysis:
I. Standard Systems & Application Scope
1.IEC Standards (International)
Basis: International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards (e.g., IEC 62271 series), emphasizing global applicability for medium-voltage (3.6 kV–40.5 kV) and low-voltage (≤1,000 V) switchgear.
Typical Applications: Widely used in global power systems, covering primary distribution (e.g., substation feeders) and secondary distribution (e.g., load distribution).
2.UL Standards (North America Focus)
Key Classifications:
UL 1558: Covers metal-enclosed low-voltage power circuit breaker switchgear for primary distribution (e.g., downstream of transformers). Rated up to 10 kA continuous current, 200 kA short-time withstand current, designed for complex protection schemes.
UL 891: Applies to dead-front switchboards for secondary distribution (e.g., direct load supply). Bus ratings ≤6 kA, short-time withstand ≤100 kA, optimized for simplified distribution and manual operation.
Regional Compliance: Aligns with North American Electrical Codes (NEC, CSA), primarily adopted in North America and UL-recognized regions.
II. Structural Design Differences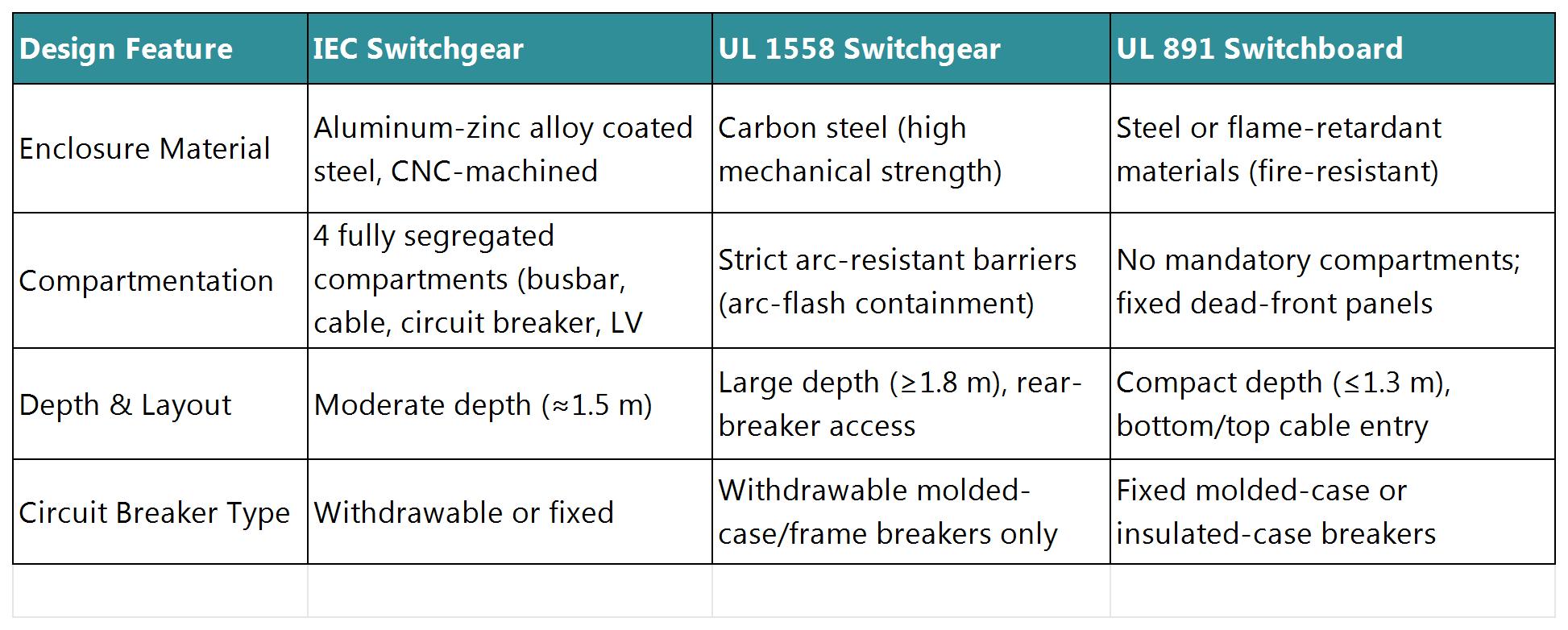
Examples:
IEC switchgear (e.g., MVnex) supports multi-cable parallel connections (3×630 mm² single-core cables per phase), cable termination height 650 mm.
UL 1558 requires top-mounted lifting devices for breaker installation; UL 891 features simplified structures for wall-mounted applications.
III. Performance Parameters & Safety Requirements
1.Short-Circuit Withstand Capability
UL 1558: Mandates 0.5-second short-time current withstand test (e.g., 200 kA) and IEEE C37.20.7 arc-fault containment validation.
UL 891: Requires only 0.05-second short-time withstand; no mandatory arc-fault testing.
IEC: Emphasizes dynamic stability (peak withstand = 2.6 × short-time current at 60 Hz) and environmental correction for dielectric tests.
2.Protection & Interlocking
IEC: Enclosure protection ≥ IP4X, compartment barriers ≥ IP2X; standardized interlocking (e.g., position selector switches to prevent misoperation).
UL 1558: Enforces “five-safety” interlocks (e.g., drawout breaker position interlocks); fully insulated busbars required.
UL 891: Focuses on operator safety (e.g., touch-safe dead-front covers); no complex interlocks.
IV. Application Scenarios & Selection Guidance
UL 1558 Switchgear:
Ideal for primary distribution in industrial/data centers (transformer capacity: 500 kVA–20 MVA), high-fault current applications requiring motorized operation.
UL 891 Switchboards:
Suited for commercial buildings/secondary distribution with space constraints, direct load connections ≤6 kA.
IEC Switchgear:
Globally adaptable, preferred for harsh environments (e.g., high humidity/sealing), multi-cable configurations, or export projects.
Summary: Key Differences & Selection Criteria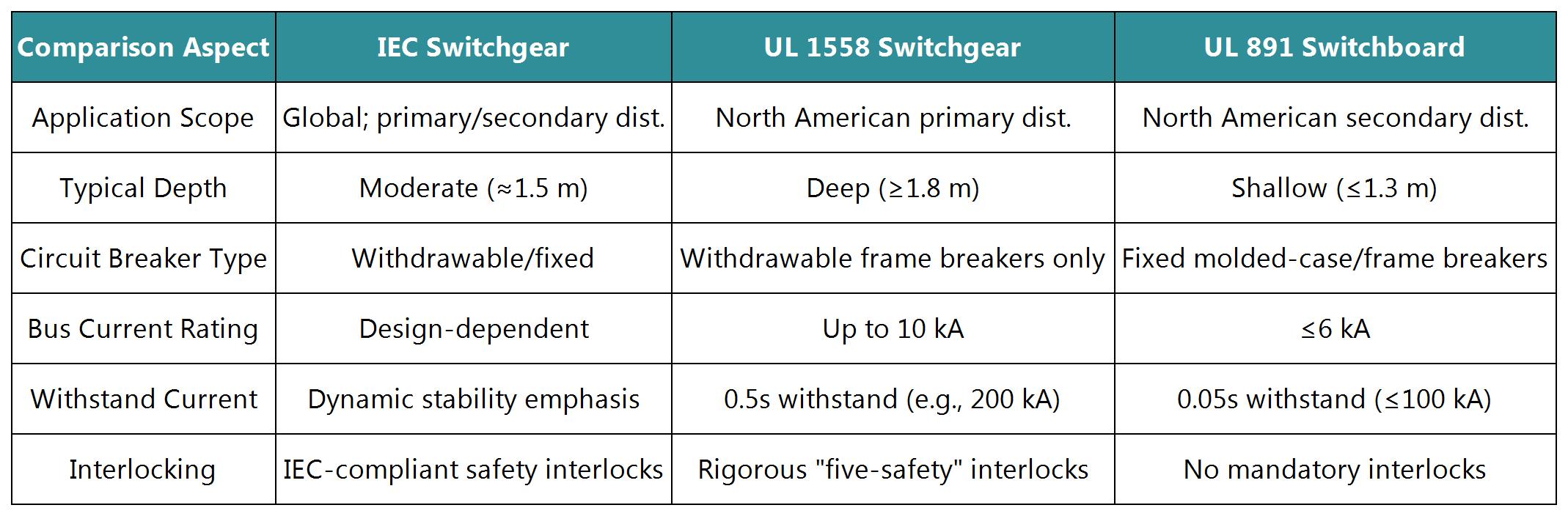
Selection Considerations:
Regional Compliance: Prioritize UL certification for North America; IEC for global projects.
System Complexity: Primary distribution/high-fault scenarios: UL 1558 or high-spec IEC; simple distribution: UL 891.
Environmental Needs: High IP protection (dust/moisture): IEC; space-constrained sites: UL 891.








