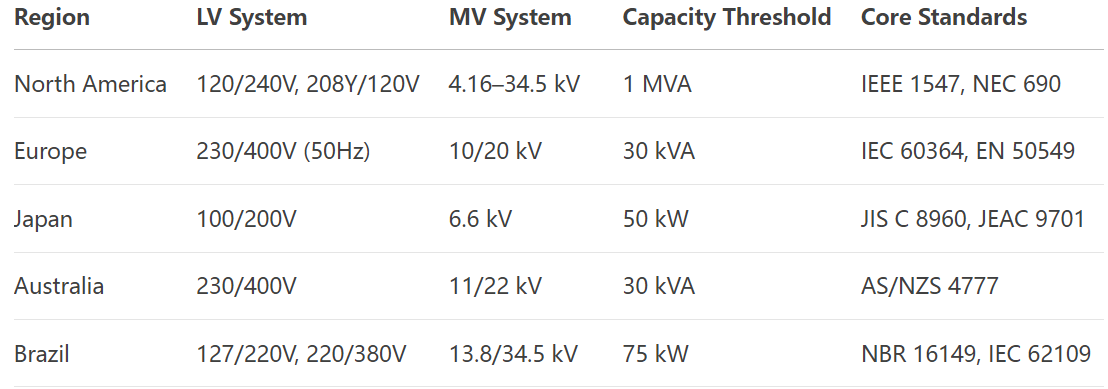
1. North America (IEEE Standard System)
Grid-Connection Voltage Levels
Low Voltage (LV) Connection
Single-Phase Systems: 120 V (phase-to-neutral) / 240 V (phase-to-phase), compliant with NEC Article 690.
Three-Phase Systems: 208Y/120 V (wye-connected), 480 V (delta-connected), with a typical commercial system limit of 1 MVA.
Standards: IEEE 1547-2018 (interconnection), UL 1741 (inverter certification).
Medium Voltage (MV) Connection
Typical Voltages: 4.16 kV (delta), 12.47 kV/13.2 kV (wye), 34.5 kV (sub-transmission).
Capacity Threshold: Most states require systems >1 MVA to connect to MV distribution (per Utility Tariff).
Key Technical Requirements
Anti-Islanding Protection: Must comply with IEEE 1547-2018 Unintentional Islanding requirements.
Voltage Regulation: Point of common coupling (PCC) voltage must adhere to ANSI C84.1 (±5% of nominal).
2. Europe (IEC Standard System)
Grid-Connection Voltage Levels
LV Connection (IEC 60364/EN 50438)
Three-Phase Systems: 400 V (phase-to-phase, 50 Hz), single-phase 230 V (phase-to-neutral).
Capacity Limits:
Germany: ≤30 kVA under VDE-AR-N 4105.
France: ≤36 kVA (three-phase) per EN 50549-1.
MV Connection
Voltage Levels: 10 kV, 20 kV (IEC 60038), with 22 kV in some Nordic countries.
Grid Code Compliance: Must meet ENTSO-E Network Code for Requirements for Generators (RfG).
Core Standards
Harmonic Distortion: THDv <3% (IEC 61000-3-6).
Fault Ride-Through: LVRT capability per EU Regulation 2016/631.
3. Australia/New Zealand (AS/NZS Standards)
Grid-Connection Voltage Levels
LV Connection (AS/NZS 4777.2)
Voltage: 230/400 V (3P4W), with single-phase ≤10 kVA, three-phase ≤30 kVA (DNSP approval required).
MV Connection
Voltage Levels: 11 kV (urban distribution), 22 kV (rural distribution).
Special Requirements
Frequency Response: Inverters must support 57–52 Hz range (AS/NZS 4777.1).
DC Injection: <0.5% rated output current (AS/NZS 4777.2 Clause 5.5.3).
4. Japan (JIS/IEC Hybrid Standards)
Grid-Connection Voltage Levels
LV Connection (JIS C 8960)
Single-Phase: 100 V (legacy)/200 V (modern, phase-to-phase).
Three-Phase: 200 V (delta-connected), ≤50 kW.
High Voltage (HV) Connection
Voltage Levels: 6.6 kV (standard distribution voltage, JEC-2300).
Key Technologies
Reverse Power Flow Control: Systems >50 kW require Reverse Power Flow Relay (JEAC 9701).
Voltage Regulation: PCC voltage ≤101% nominal (JET C0).
5. Other Key Regions
India (IS/IEC Standards)
LV: 415 V (3P4W), 240 V (1P2W), ≤10 kW (CEA Regulation 2020).
MV: 11 kV (distribution), 33 kV (primary distribution), per IS 16169 harmonics.
Brazil (NBR/IEC Standards)
LV: 127 V/220 V (1P), 220 V/380 V (3P), ≤75 kW (ANEEL REN 482).
MV: 13.8 kV (wye), 34.5 kV (sub-transmission).
International Standards Comparison
Engineering Notes
Terminology Precision:
Specify connection type (e.g., “208Y/120 V” instead of “208V”).
Distinguish distribution voltage (e.g., 11 kV) from sub-transmission voltage (e.g., 34.5 kV).
Standard Hierarchy:
National codes (e.g., VDE) > Regional (EN) > International (IEC).
Emerging Trends:
Dynamic Voltage Restorers (DVR) in MV systems (IEEE 1547-2022).
400V DC microgrids in Europe (IEC 62898-2).
Data Sources: IEC 60038 (standard voltages), latest grid regulations (as of Q1 2024). For country-specific details (e.g., South Africa NRS 097-2), further information can be provided.








