1. Definition & Classification
1.1 RMU (Ring Main Unit) Switchgear
Definition
A compact, modular medium-voltage (MV) switchgear designed for ring-main distribution networks, primarily utilizing load-switching devices (e.g., load break switches, fuse combinations) rather than high-breaking-capacity circuit breakers.
Key Standards
IEC 62271-200 (AC metal-enclosed switchgear for rated voltages above 1 kV and up to and including 52 kV)
Types
Air-Insulated RMU:Uses atmospheric air as the primary insulation medium.
SF6-Insulated RMU:Relies on SF6 gas for insulation and arc quenching.
Solid-Insulated RMU:Utilizes epoxy resin or other solid dielectrics.
1.2 SF6 Switchgear
Definition
A switchgear where sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas serves as the primary insulation and arc-quenching medium, applicable in both RMU and circuit-breaker-based systems.
Key Standards
IEC 62271-203 (Gas-insulated metal-enclosed switchgear for rated voltages above 52 kV)
IEEE C37.122 (IEEE Standard for High-Voltage Gas-Insulated Substations)
Types
SF6 Ring Main Unit : Compact RMU with SF6 insulation (e.g., Schneider SM6, ABB SafeRing).
SF6 Gas-Insulated Switchgear : High-voltage switchgear with SF6-insulated breakers (e.g., Siemens 8DN8, Hitachi GX series).
2. Core Technical Differences
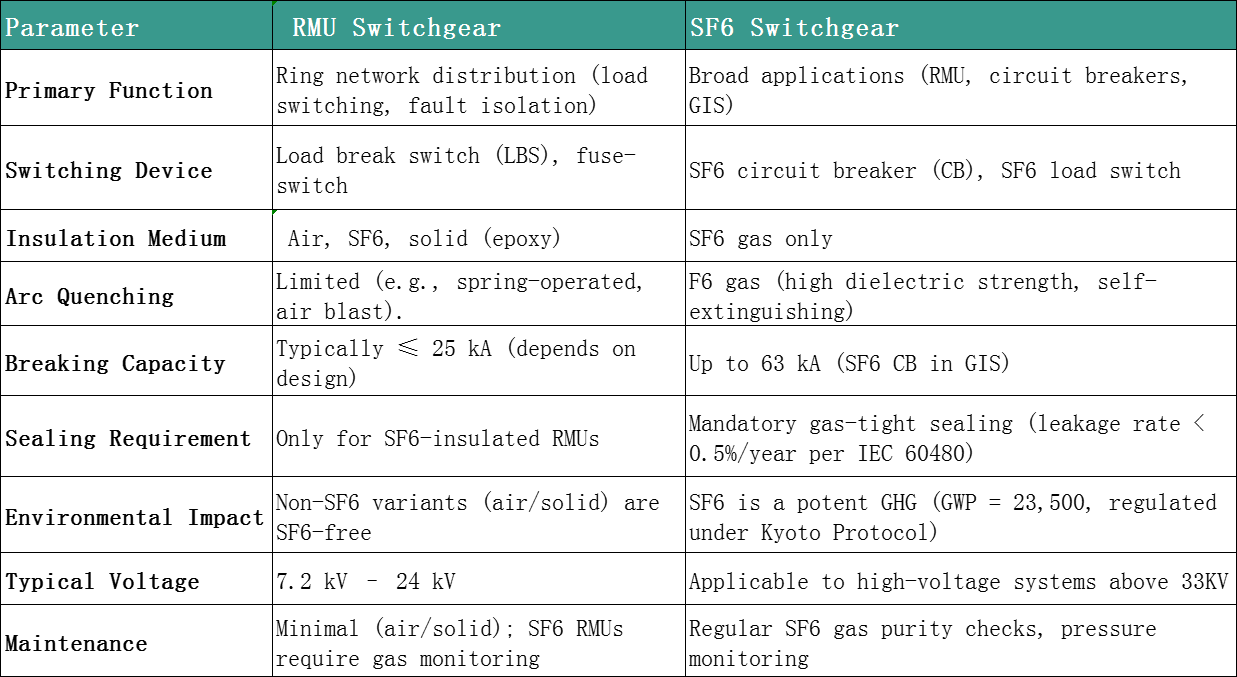
3. Application Scenarios
3.1 RMU Switchgear
Urban distribution networks: Ring-main systems, cable branches.
Industrial plants: Compact substations, transformer protection.
Renewable energy: Solar/wind farm grid connections.
3.2 SF6 Switchgear
High-voltage substations: GIS for 72.5 kV and above.
Railway electrification: High-breaking-capacity requirements.
Data centers: SF6 RMUs for space-saving designs.
4. Advantages & Disadvantages
4.1 RMU Switchgear
Pros:
Compact, cost-effective for distribution.
SF6-free options (air/solid) align with F-gas regulations.
Cons:
Limited fault current interruption (e.g., 20 kA vs. SF6 CB’s 63 kA).
4.2 SF6 Switchgear
Pros:
Superior dielectric strength (3× air at 0.3 MPa).
High breaking capacity (63 kA+).
Cons:
SF6 emissions risk (EU F-gas Regulation 517/2014 mandates strict handling).
Higher lifecycle cost (gas recycling, maintenance).








