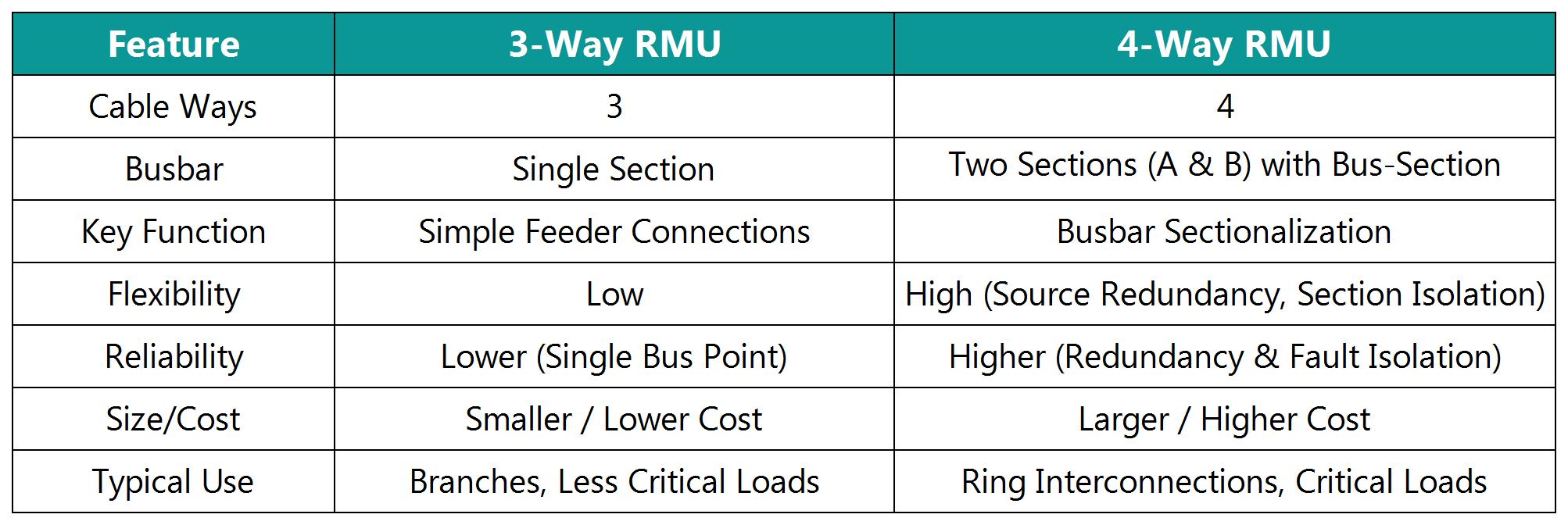
The difference between 3-way and 4-way Ring Main Units (RMUs) lies primarily in the number of cable compartments and the configuration of the internal busbar, which directly impact flexibility, reliability, and application. Here’s a breakdown:

1.Number of Ways / Cable Compartments:
3-Way RMU: Has three cable connection compartments.
4-Way RMU: Has four cable connection compartments.
2.Busbar Configuration:
3-Way RMU: Typically has a single, non-segmented busbar running through the unit. All three ways connect to this single busbar section.
4-Way RMU: Includes an integrated bus-section switch or isolator. This splits the internal busbar into two separate sections (Section A and Section B). The fourth way is specifically for this bus-section switch/isolation function.
3.Functional Purpose & Flexibility:
1)3-Way RMU:
Used for simple feeder connections.
Common configurations: 1 Incomer (source) + 1 Outgoing Feeder + 1 Transformer Feeder OR 2 Outgoing Feeders + 1 Transformer Feeder.
All loads/transformers are connected to the same single busbar section.
Limitation: A fault on the busbar itself or the need for maintenance requires the entire RMU and all connected loads to be taken out of service.
2)4-Way RMU:
The key feature is the bus-section switch/isolation function (the 4th way).
his allows the busbar to be split into two independent sections (Section A and Section B).
Enables connection of two independent incoming sources (e.g., two different feeders from the ring) – one to Section A, one to Section B.
Outgoing feeders/transformers can then be connected to either Section A or Section B.
Critical Advantage: The bus-section switch allows:
Isolation: One section (A or B) can be isolated for maintenance or repair while the other section remains live and supplies its connected loads.
Fault Containment: A fault occurring on one busbar section (or a feeder connected to it) can be isolated, allowing the other section and its loads to remain operational.
Source Redundancy: Enables true N-1 or similar redundancy schemes by feeding from two separate sources.
4.Reliability & Continuity of Supply:
3-Way RMU: Offers lower reliability for the connected loads if the busbar fails or needs maintenance. All loads lose supply.
4-Way RMU: Offers significantly higher reliability and continuity of supply. The ability to isolate half the busbar means only the loads on the faulted/maintenance section lose power, while the other half stays online.
5.Physical Size and Cost:
3-Way RMU: More compact and generally less expensive due to fewer compartments and simpler busbar.
4-Way RMU: Larger footprint (due to the extra compartment) and more expensive because of the added complexity of the bus-section switching/isolation mechanism.
6.Typical Applications:
3-Way RMU: Ideal for smaller substations, branch points on the network, or supplying less critical loads where the cost/space saving is a priority and brief outages affecting all loads are acceptable for busbar work.
4-Way RMU: Essential for critical substations, points where two feeders meet (like a true ring interconnection point), or feeding important loads requiring higher supply continuity. Used where network reliability standards demand busbar sectionalization.
In essence: The 4-way RMU adds the crucial bus-section switching capability that the 3-way lacks. This single feature provides significantly enhanced operational flexibility, fault management, and supply reliability, making it necessary for critical network nodes, albeit at a higher cost and size. The 3-way RMU is a simpler, more economical solution for less critical points in the distribution network.








