Photovoltaic DC combiner boxes and AC combiner boxes are key components in PV systems for power consolidation, but they differ significantly in function, structure, and application. Below is a detailed comparison:
1. Current Type & Location in the System
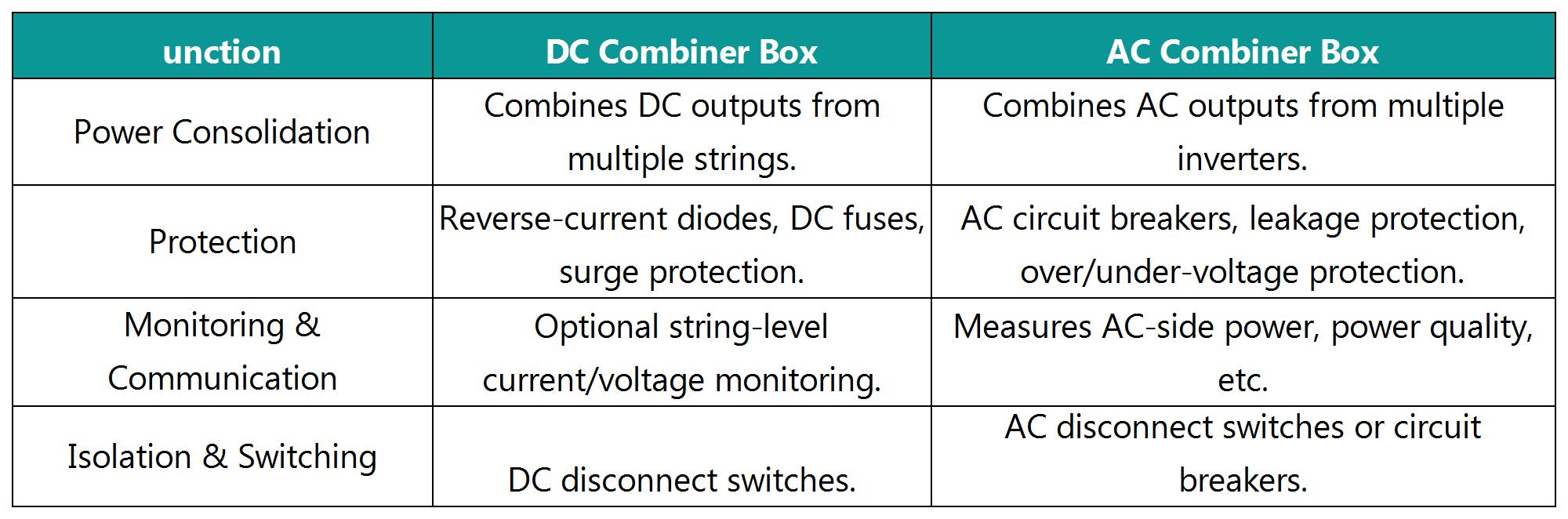
DC Combiner Box
Current Type: Handles direct current (DC).
Location: Positioned between PV modules and the inverter, combining multiple PV string outputs (e.g., 12–20 strings) before feeding them into the inverter.
Typical Voltage: Input voltage matches the DC high voltage of the strings (e.g., 600V–1500V).
AC Combiner Box
Current Type: Handles alternating current (AC).
Location: Located between the inverter output and the grid/load, consolidating AC outputs from multiple inverters (e.g., 380V/400V three-phase) before connecting to distribution panels or transformers.
Typical Voltage: Low-voltage AC (e.g., 230V single-phase or 400V three-phase).
2. Core Functional Differences
3. Internal Structure Features
DC Combiner Box:
Must address DC arc risks (harder to extinguish), requiring specialized DC breakers/fuses.
May include MPPT optimizers (in some systems).
AC Combiner Box:
Resembles traditional power distribution panels, with AC breakers, meters, etc.
Requires phase balancing (in three-phase systems).
4. Application Scenarios
DC Combiner Box:
Used in centralized or string inverter systems.
Common in large-scale ground-mounted or commercial rooftop PV plants.
AC Combiner Box:
Used when multiple inverters operate in parallel (e.g., distributed generation).
Microinverter systems typically skip DC combiner boxes but may need AC combiner boxes.
5. Safety & Standards
DC Side Risks: High DC voltage increases arc fault hazards, demanding higher insulation and protection levels.
AC Side Standards: Must comply with AC power distribution norms (e.g., IEC 60364).
Summary
DC Combiner Boxes are unique to PV systems, managing DC-side consolidation and protection.
AC Combiner Boxes function as standard AC distribution units, compatible with conventional power systems.
The two complement each other, ensuring safe and efficient grid integration of solar power.








