Switchgear, as a critical component of power systems, has evolved alongside advancements in electrical engineering, materials science, and automation technology. Below is an overview of the key stages and technological developments in switchgear history.
1. Early Stages (Late 19th Century – Early 20th Century)
Background: Power systems were in their infancy, operating at low voltages (DC or low-voltage AC).
Characteristics:
Simple knife switches and fuses mounted on wooden or metal frames.
No enclosed design, poor safety, and susceptibility to environmental factors.
Manual operation with no protection features.
2. Emergence of Metal-Enclosed Switchgear (1920s–1940s)
Technological Advances:
Metal enclosures replaced wooden structures, improving fire resistance and mechanical strength.
Air insulation was dominant, and oil circuit breakers were introduced.
Applications:
Standardized designs for medium-voltage grids (3.6–15 kV).
Fixed-type switchgear required power shutdown for maintenance.
3. Insulation Medium Innovations (1950s–1970s)
SF₆ Switchgear:
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆) gas insulation emerged in the 1950s, offering compact size and superior arc-quenching capabilities.
Used in high-voltage applications (72.5 kV and above).
Vacuum Circuit Breakers:
Vacuum interrupter technology matured in the 1960s, replacing oil circuit breakers due to maintenance-free operation and long lifespan.
Armored and Withdrawable Designs:
Modular structures with removable circuit breakers (e.g., KYN series) simplified maintenance.
4. Intelligent and Automated Switchgear (1980s–2000s)
Microprocessor-Based Protection:
Integrated relay protection, fault diagnostics, and communication (e.g., IEC 61850 standard).
Smart Switchgear:
Equipped with sensors (temperature, partial discharge monitoring) and remote control (SCADA systems).
Environmental Considerations:
Reduced SF₆ usage (due to greenhouse effect) and adoption of dry air or nitrogen insulation.
5. Modern Technological Integration (2010s–Present)
Digitalization and IoT:
AI-driven predictive maintenance and digital twin technology.
Cloud-based data management for smart grid compatibility.
Compact Designs:
Solid-insulated switchgear (SIS) eliminates gas leakage risks.
Renewable Energy Adaptation:
Optimized for frequent switching in wind/solar power and DC distribution.
Comparison of Switchgear Types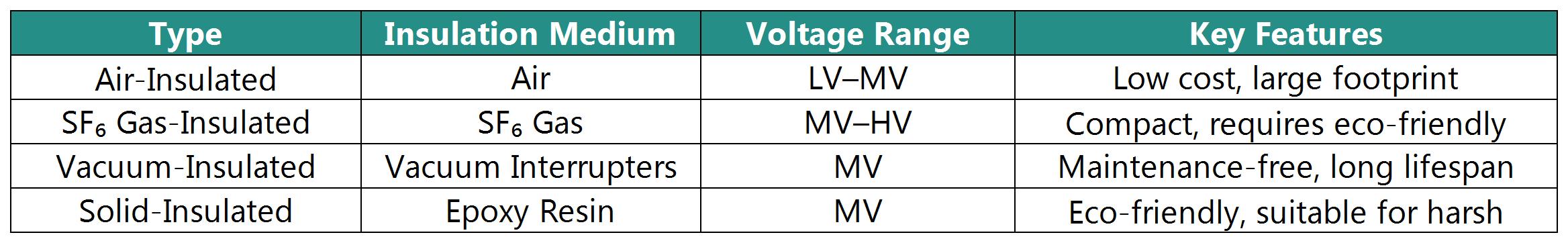
Future Trends
Green Solutions: Development of SF₆-free insulation technologies.
Smart Integration: AI and edge computing for real-time monitoring.
High Reliability: Resilience against extreme weather and complex grid conditions.
DC Switchgear: Support for renewable energy storage and DC microgrids.
The evolution of switchgear reflects the power industry’s pursuit of safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Future advancements will continue to focus on smarter, greener, and more reliable solutions.








