Introduction to Generator Loss-of-Excitation Protection
GWZC-9886 Generator Backup Protection Relay features generator loss-of-field protection function. Generator loss-of-excitation protection serves as a critical defense against generator excitation current failure caused by excitation system faults. As vital protection against system oscillations, terminal equipment damage, and reverse flow of reactive power during asynchronous operation.
I. Loss-of-Field Fault Mechanism & Hazards
Principle
Loss of excitation current → Generator EMF decay → Loss of synchronous torque → Transition to asynchronous operation (slip operation)
Formula: Synchronous torque T sync∝ X dE f V s sinδ → E f→0 during field loss
Critical Hazards
Grid impact: Absorbs reactive power up to 2× rated capacity (risk of voltage collapse)
Generator damage: Rotor overheating (eddy current losses), stator overcurrent (asymmetric torque pulsation), mechanical vibration
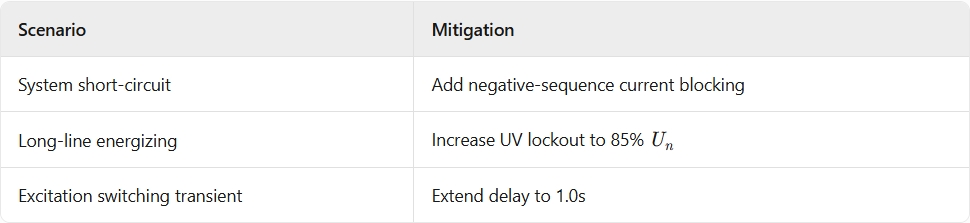
II. Protection Operating Criteria (Primary Schemes)
Setting Requirements:
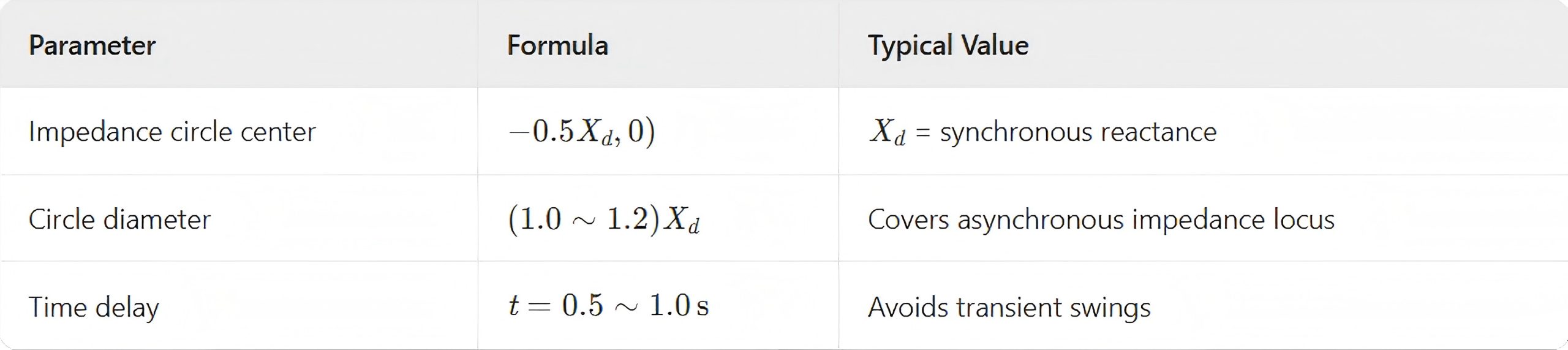
Auxiliary Criteria:
Undervoltage lockout: Enable protection when terminal voltage <80% U n
Negative-sequence blocking: Immunity to asymmetrical faults
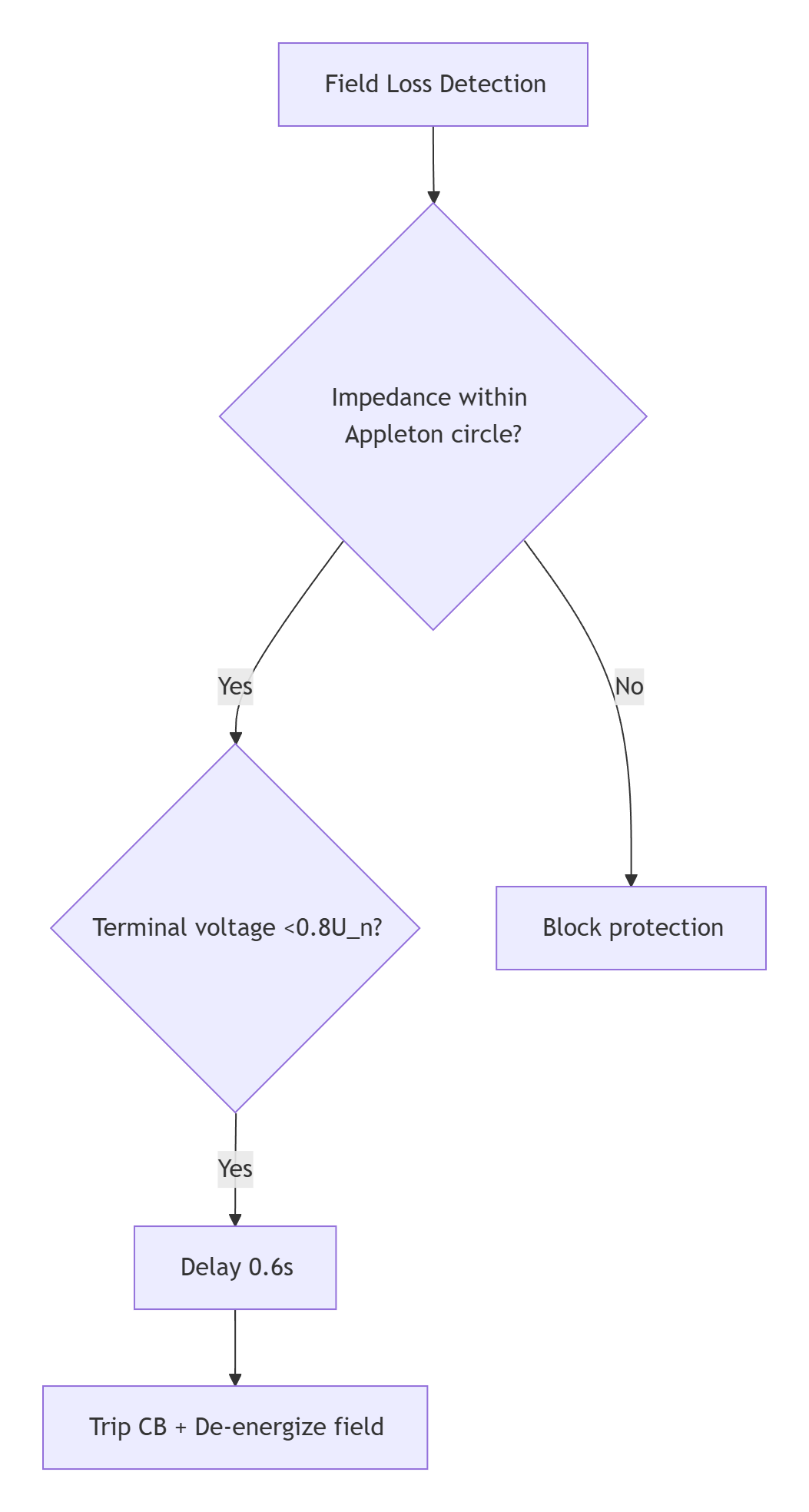
III. Standardized Configuration (Example: Pumped Storage Plant)
IV. Key Maintenance Practices
Setting Verification
Static tests: Inject 50%-100% rated current to validate impedance boundaries
Dynamic simulation: RTDS modeling of slip operation (slip ratio S=0.02-0.05)
False Trip Prevention