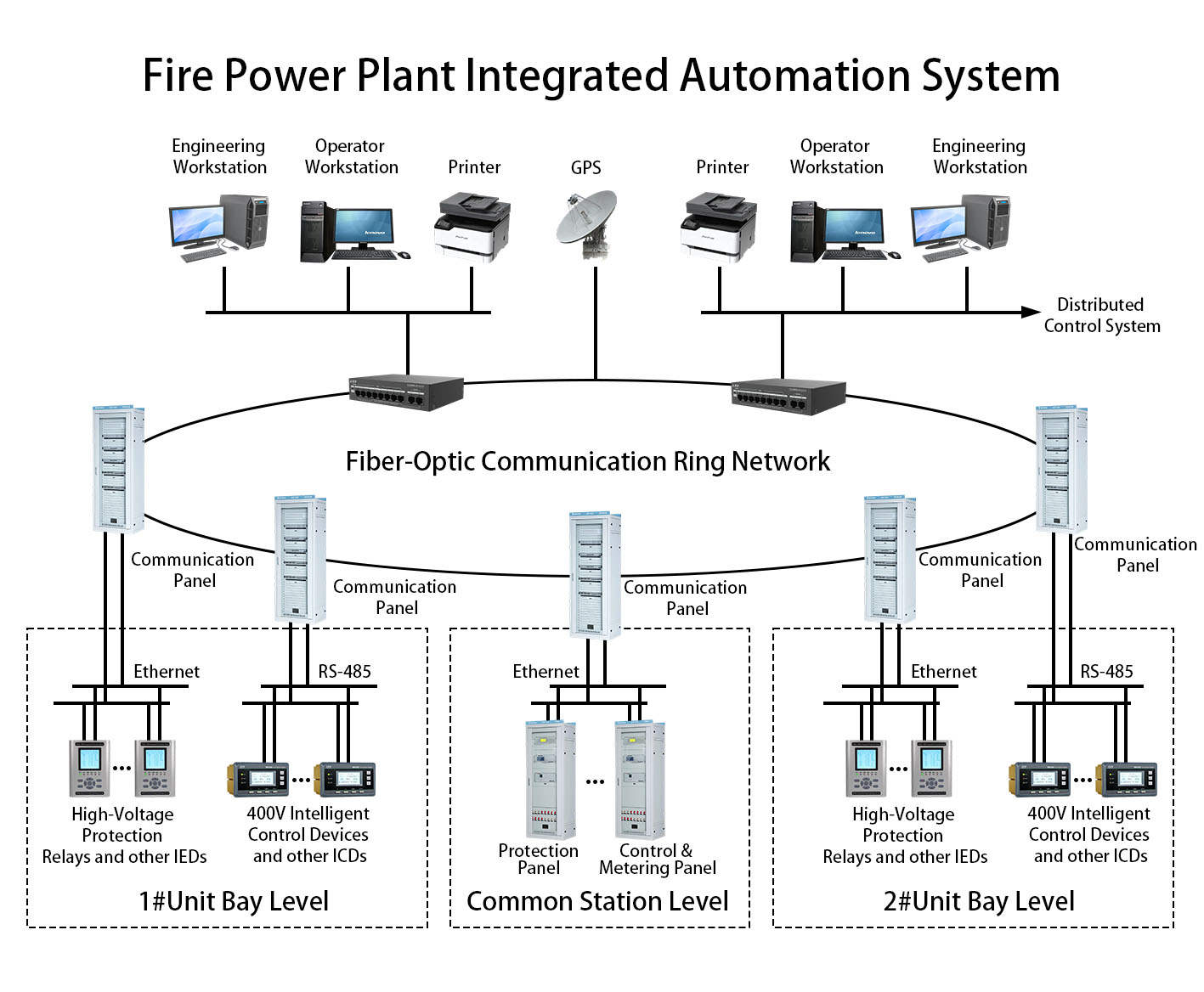
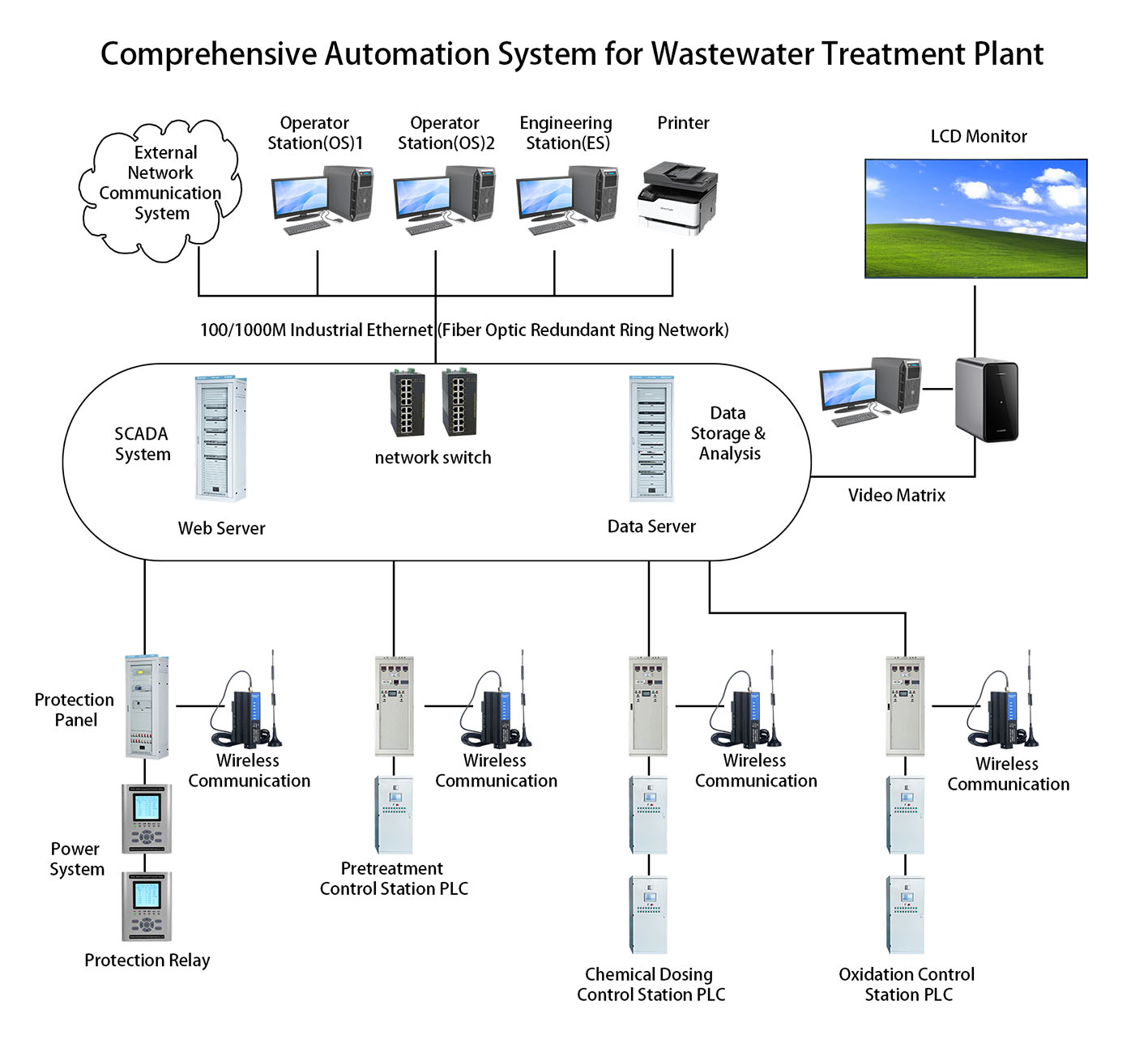
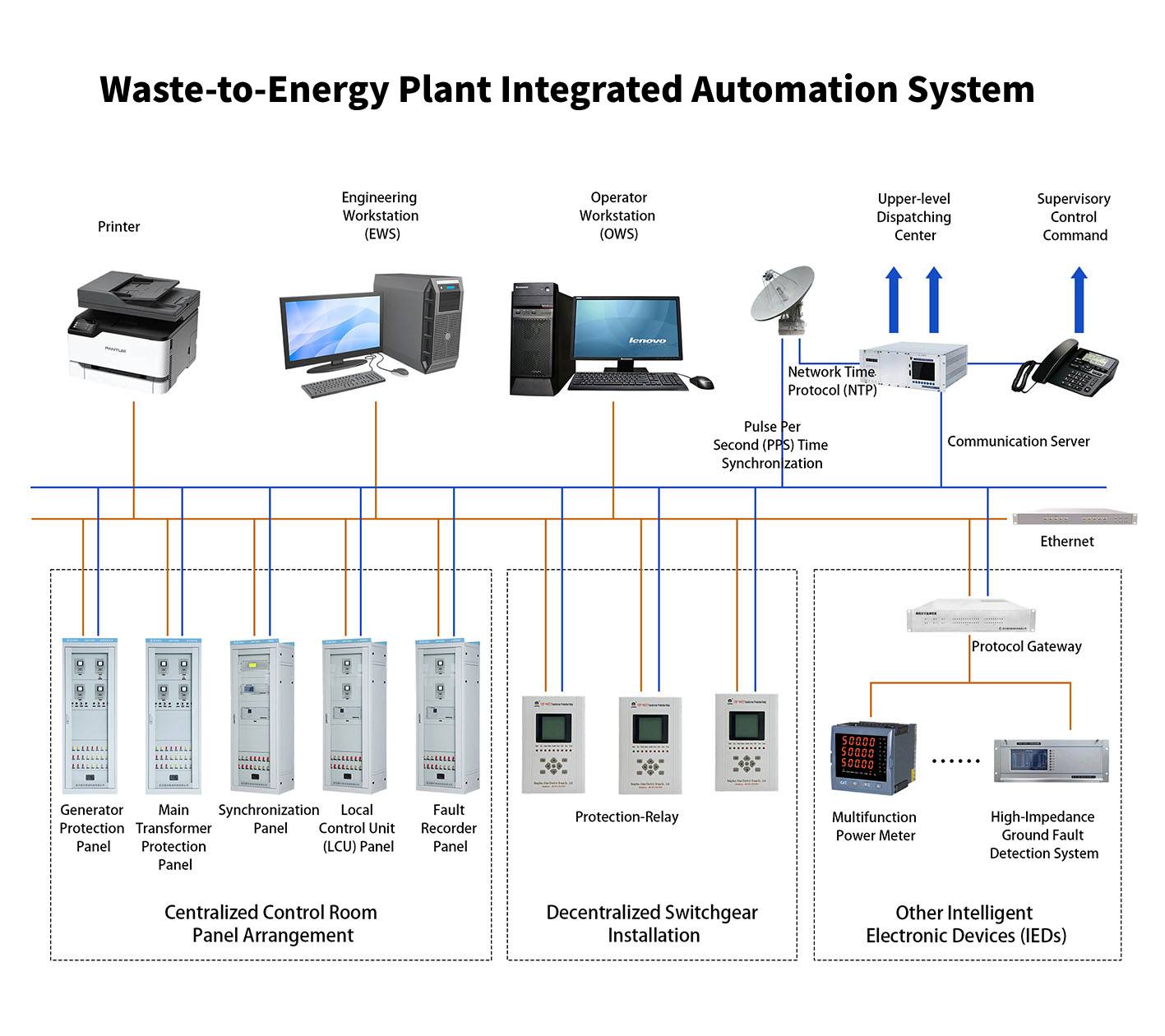
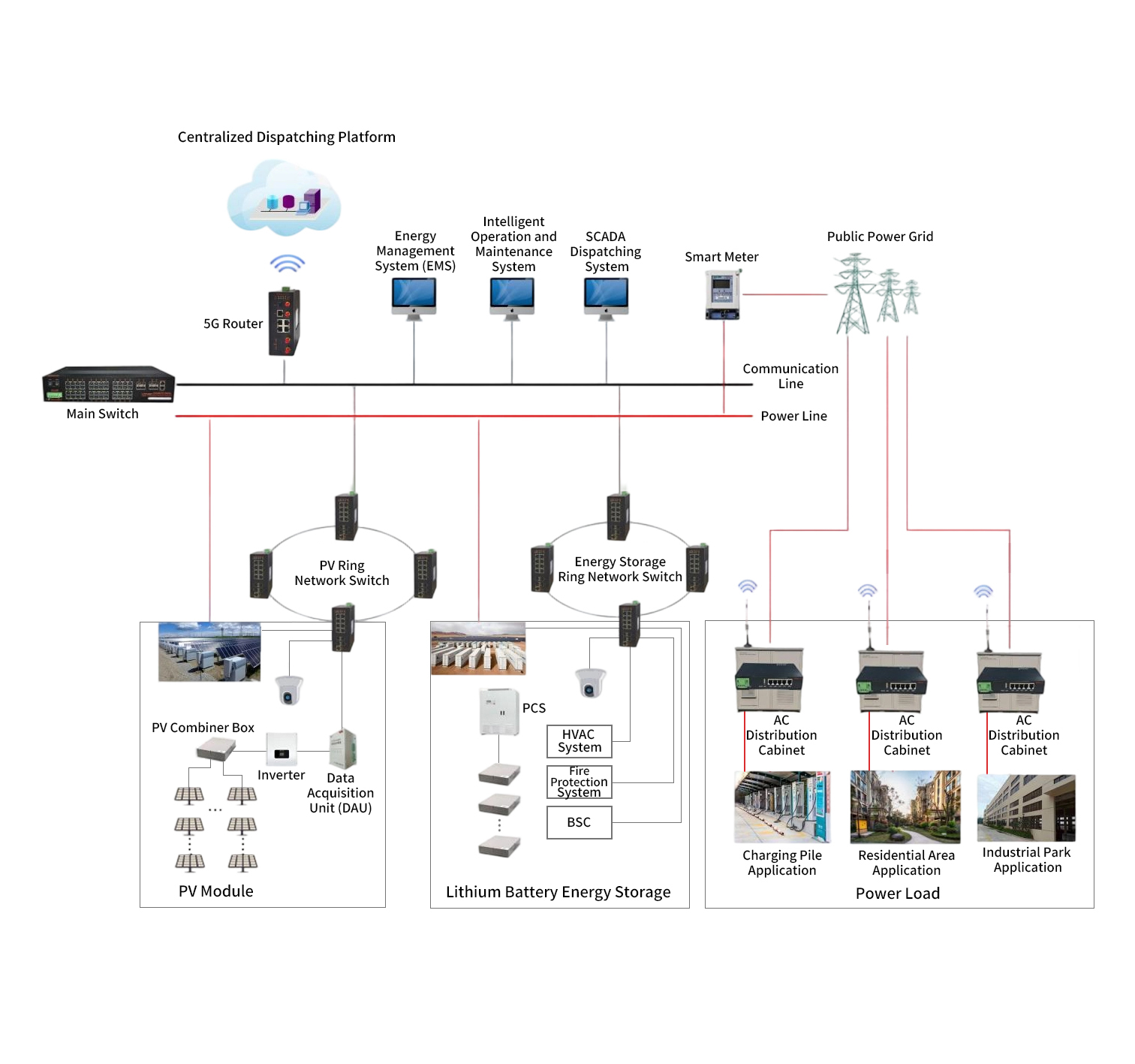
1. System Overview
The pumped storage power station integrated automation system is an intelligent management system centered around a computer monitoring system, integrating multiple functions such as protection, measurement, control, and communication. Utilizing modern computer technology, network communication technology, and automatic control technology, the system enables automated monitoring and control of the entire station’s equipment, including generating units, transformers, switchyards, and auxiliary systems, ensuring safe, reliable, and economical operation.
Key Features of the System:
Hierarchical and distributed architecture design
High reliability and redundant configuration
Support for standardized communication protocols
Comprehensive anti-misoperation functions
Intelligent diagnostics and early warning capabilities
User-friendly human-machine interface (HMI)
2. System Composition and Subsystem Functions
2.1 Overall System Architecture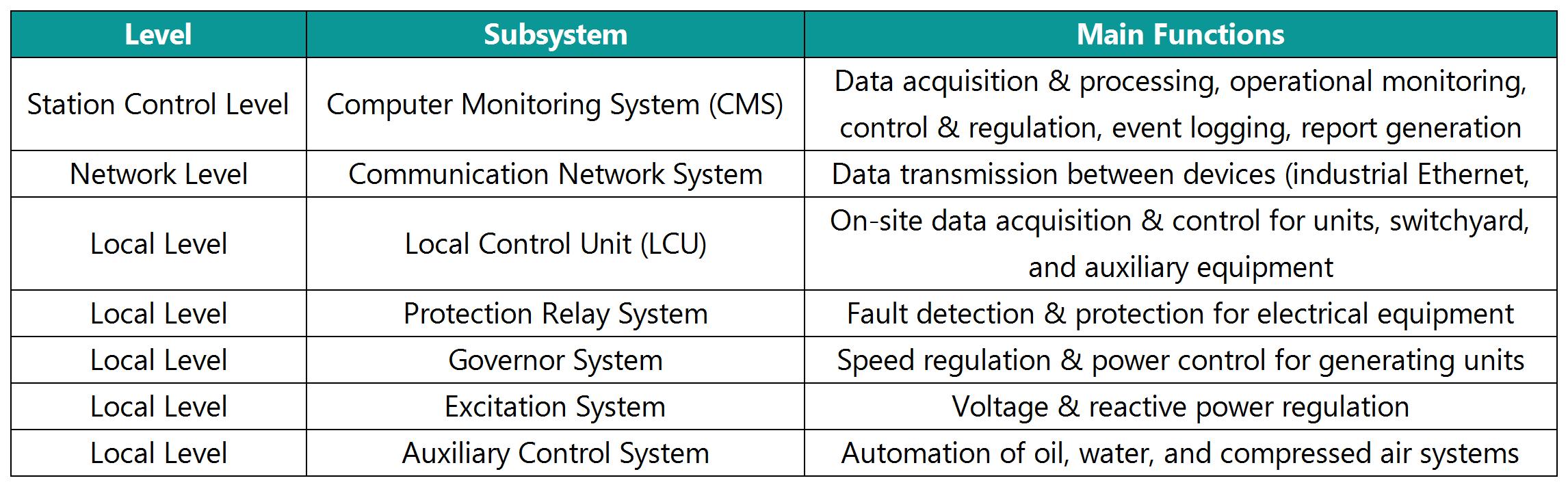
2.2 Detailed Subsystem Descriptions
2.2.1 Computer Monitoring System (CMS)
Data Acquisition & Processing (SCADA) – Real-time collection and processing of operational parameters
Operational Monitoring – Equipment status tracking, alarm management, trend analysis
Control Operations – Unit start/stop, mode transition, load adjustment
Event Logging – System events, operation records, fault recording
Report Management – Automatic generation of operational & statistical reports
Human-Machine Interface (HMI) – Graphical operation interface & historical data query
2.2.2 Protection Relay System
Generator Protection – Differential protection, overcurrent protection, loss-of-field protection
Transformer Protection – Differential protection, Buchholz relay, overload protection
Line Protection – Distance protection, overcurrent protection, auto-reclosing
Busbar Protection – Differential protection, breaker failure protection
Station Service Protection – Overcurrent & earth fault protection
2.2.3 Local Control Unit (LCU)
Unit LCU – Start/stop control, mode transition, protection interlocking
Switchyard LCU – Circuit breaker & disconnector control, voltage/reactive power regulation
Auxiliary LCU – Control of station service systems, drainage, compressed air
Gate LCU – Intake/outlet gate control & monitoring
2.2.4 Governor System
Speed & power regulation
Frequency control
Mode transition control
Protection coordination
2.2.5 Excitation System
Generator voltage regulation
Reactive power control
Field forcing & limitation functions
De-excitation & overvoltage protection
3. System Hardware & Software Configuration
3.1 Hardware Configuration
3.1.1 Station Control Level Hardware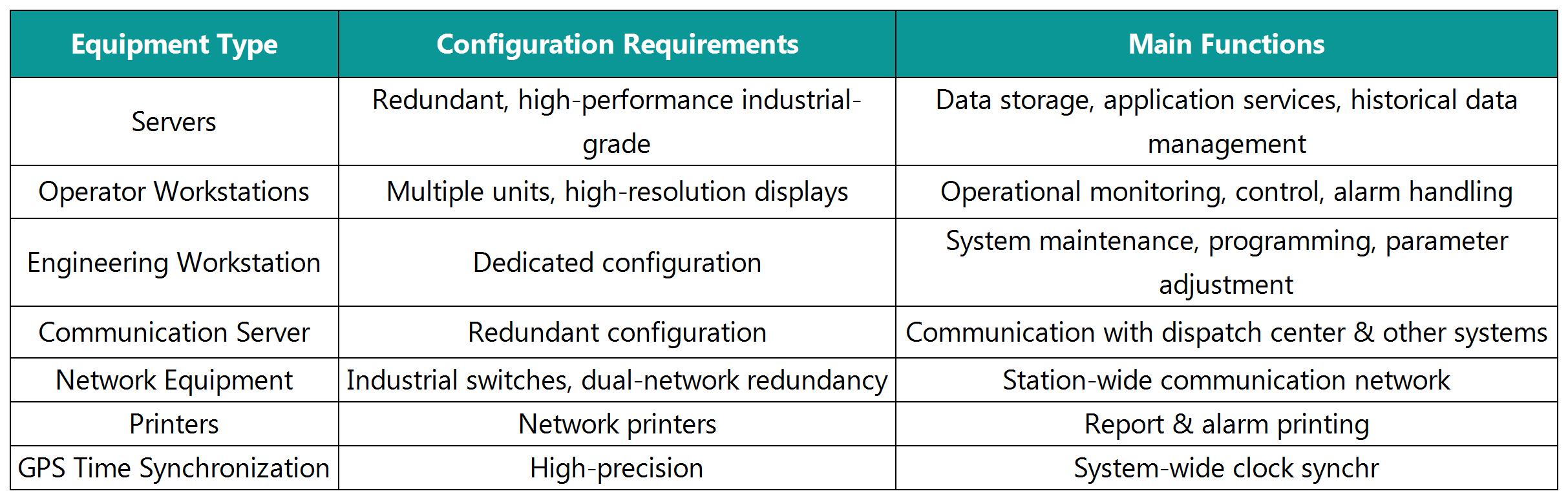
3.1.2 Local Level Hardware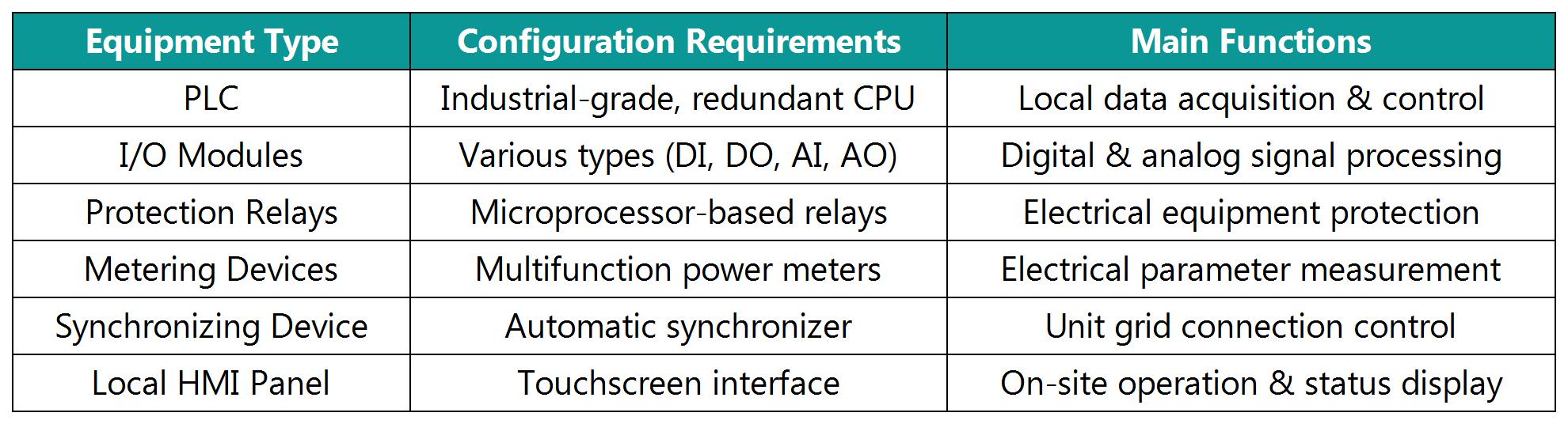 3.2 Software Configuration
3.2 Software Configuration
3.2.1 System Software
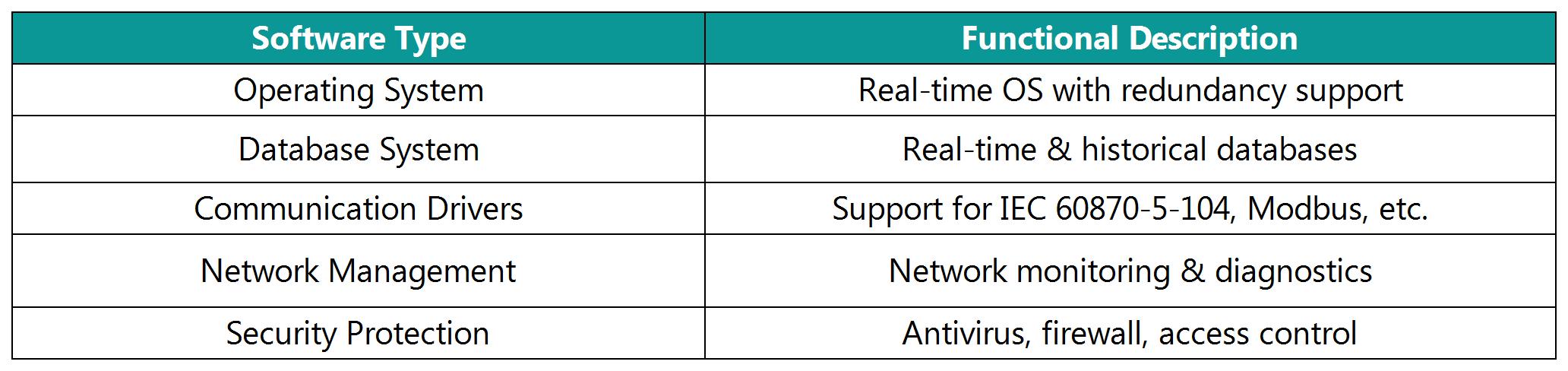
3.2.2 Application Software 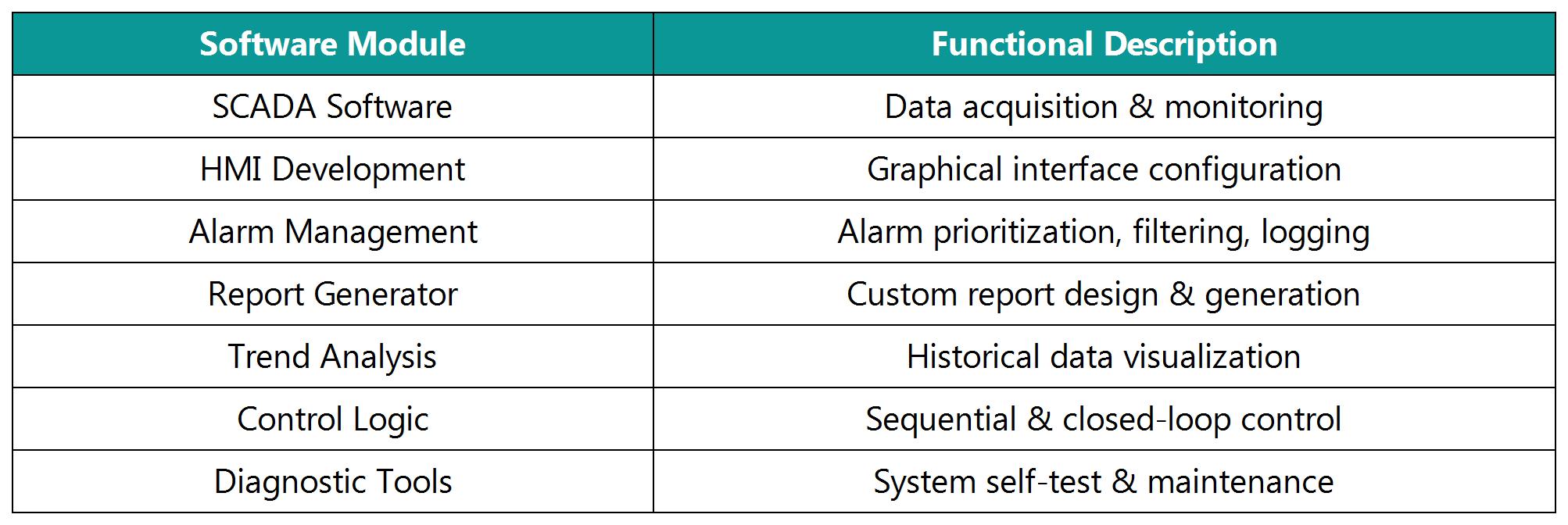
3.3 Key Equipment Technical Specifications
3.3.1 Computer Monitoring System
MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) ≥ 50,000 hours
System Availability ≥ 99.9%
Control Command Response Time < 1 sec
Screen Refresh Time < 2 sec
Dual-Network Redundancy & Hot Standby Support
3.3.2 PLC System
Scan Cycle ≤ 10 ms
IEC 61131-3 Programming Standard Compliance
Hot-Swappable Module Support
Operating Temperature Range -20°C to 60°C
Industrial-Grade EMI Immunity (Level 4)
3.3.3 Protection Relays
Protection Operation Time ≤ 30 ms
Measurement Accuracy 0.2 class
IEC 61850 Communication Protocol Support
Fault Recording Capability
Remote Setting Adjustment & Protection Enabling/Disabling
4. Key Technical Requirements
4.1 Reliability Requirements
Redundant configuration for critical equipment
Automatic fault detection & switching
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) resistance
Anti-misoperation interlocking
4.2 Real-Time Performance Requirements
Status Change Transmission to Station Level ≤ 1 sec
Analog Value Transmission (Deadband Exceeded) ≤ 2 sec
Control Command Execution Cycle ≤ 1 sec
Adjustable Screen Refresh Rate (1–3 sec)
4.3 Security Requirements
Multi-level access control
Multi-step command confirmation
Operation logging & traceability
Cybersecurity protection measures
4.4 Scalability Requirements
Support for equipment capacity expansion
Modular functional expansion capability
Additional communication interface support
Software upgrade compatibility