1. System Overview
The comprehensive automation system solution for wastewater treatment plants is an integrated management system based on modern automation control technology, computer technology, network communication technology, and intelligent sensing technology. It is designed to achieve intelligent monitoring, precise control, and efficient management of the entire wastewater treatment process. The system ensures stable operation, optimized energy consumption, and compliance with discharge standards through centralized monitoring, distributed control, data analysis, and remote maintenance, while reducing manual intervention costs and improving overall operational efficiency.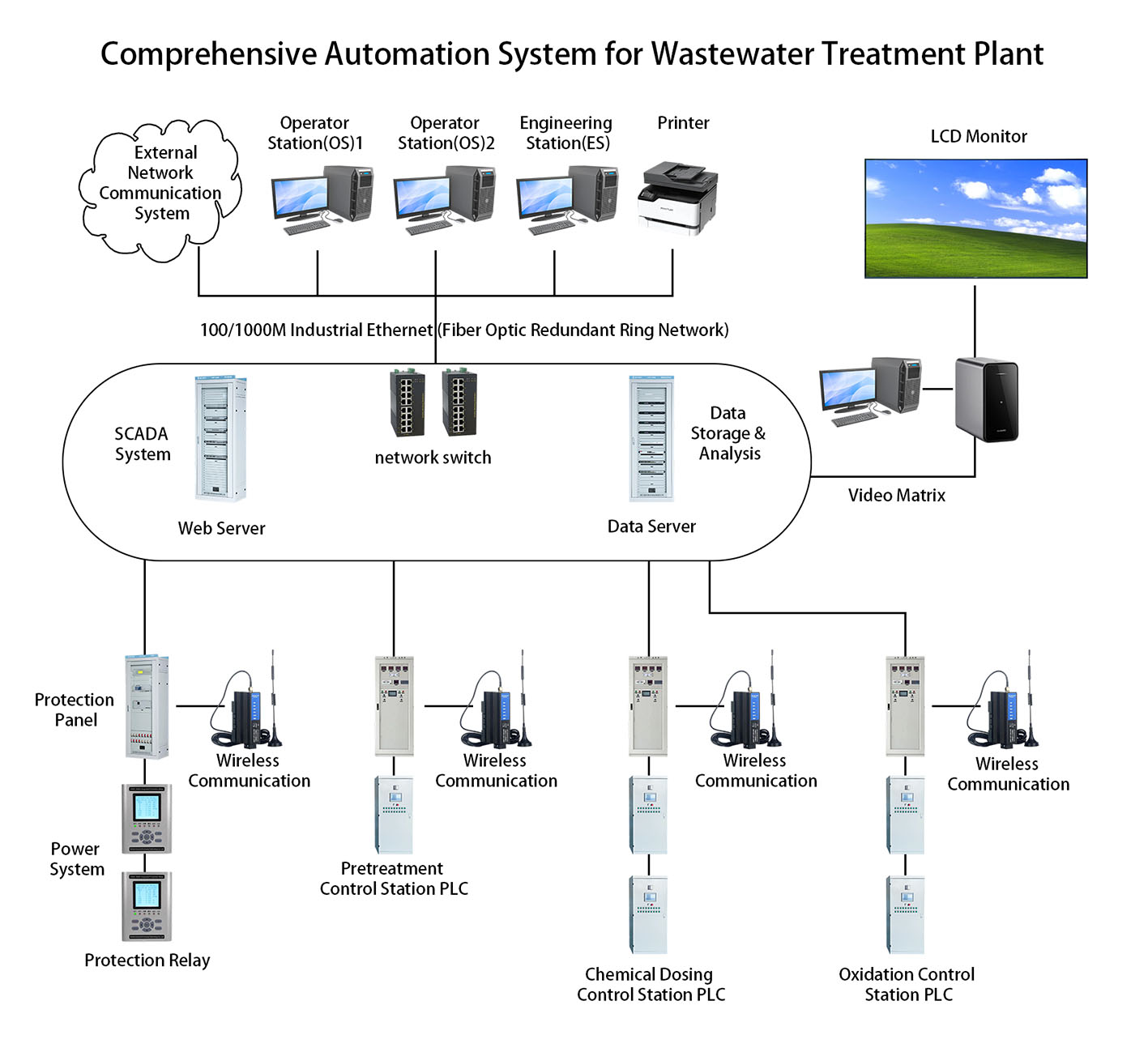
2. System Components
(1) Process Control System (PCS)
The Process Control System (PCS) is the core of wastewater treatment automation, responsible for real-time monitoring and control of various process units (e.g., screens, grit chambers, biological reactors, secondary clarifiers, disinfection tanks). Using PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and DCS (Distributed Control Systems), it enables equipment interlocking, parameter adjustment (e.g., pH, dissolved oxygen, sludge concentration), and process optimization to ensure effluent compliance.
(2) Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) System
The SCADA system serves as the human-machine interface (HMI), providing centralized monitoring, data acquisition, alarm management, and historical data storage for the entire plant. Operators can visualize equipment status, process parameters, and operational trends through graphical interfaces, with support for remote control and report generation.
(3) Instrumentation and Detection System
Includes various online monitoring instruments (e.g., flow meters, pH meters, COD/ammonia nitrogen analyzers, turbidity meters) and sensors for real-time measurement of key parameters such as water quality, flow rate, pressure, and temperature, providing data support for automated control.
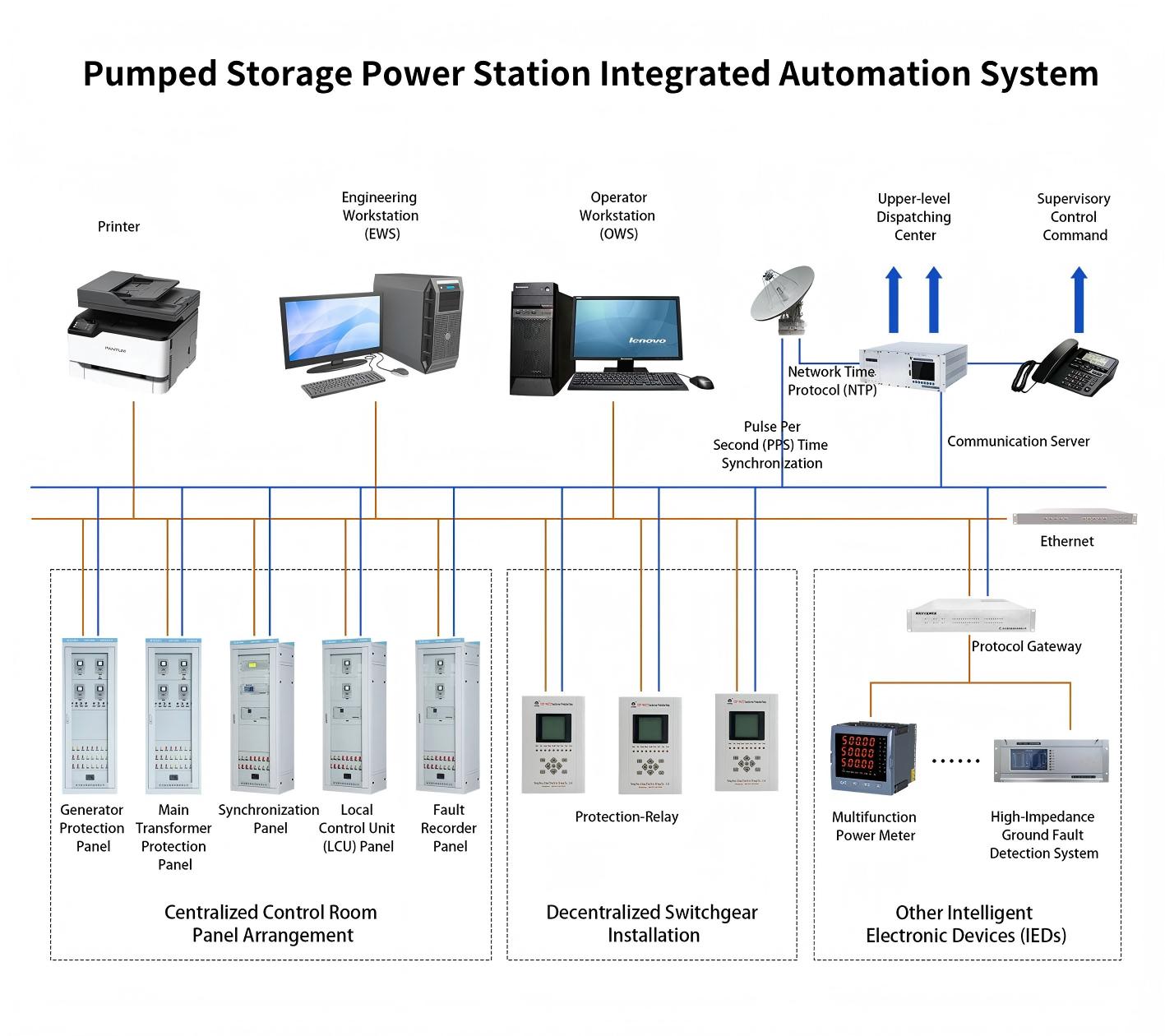
(4) Electrical Control System
Covers high/low-voltage power distribution systems, Motor Control Centers (MCCs), variable frequency drives (VFDs), and protective relays, ensuring safe power supply and stable equipment operation through start-stop control, protection mechanisms, and energy consumption management.
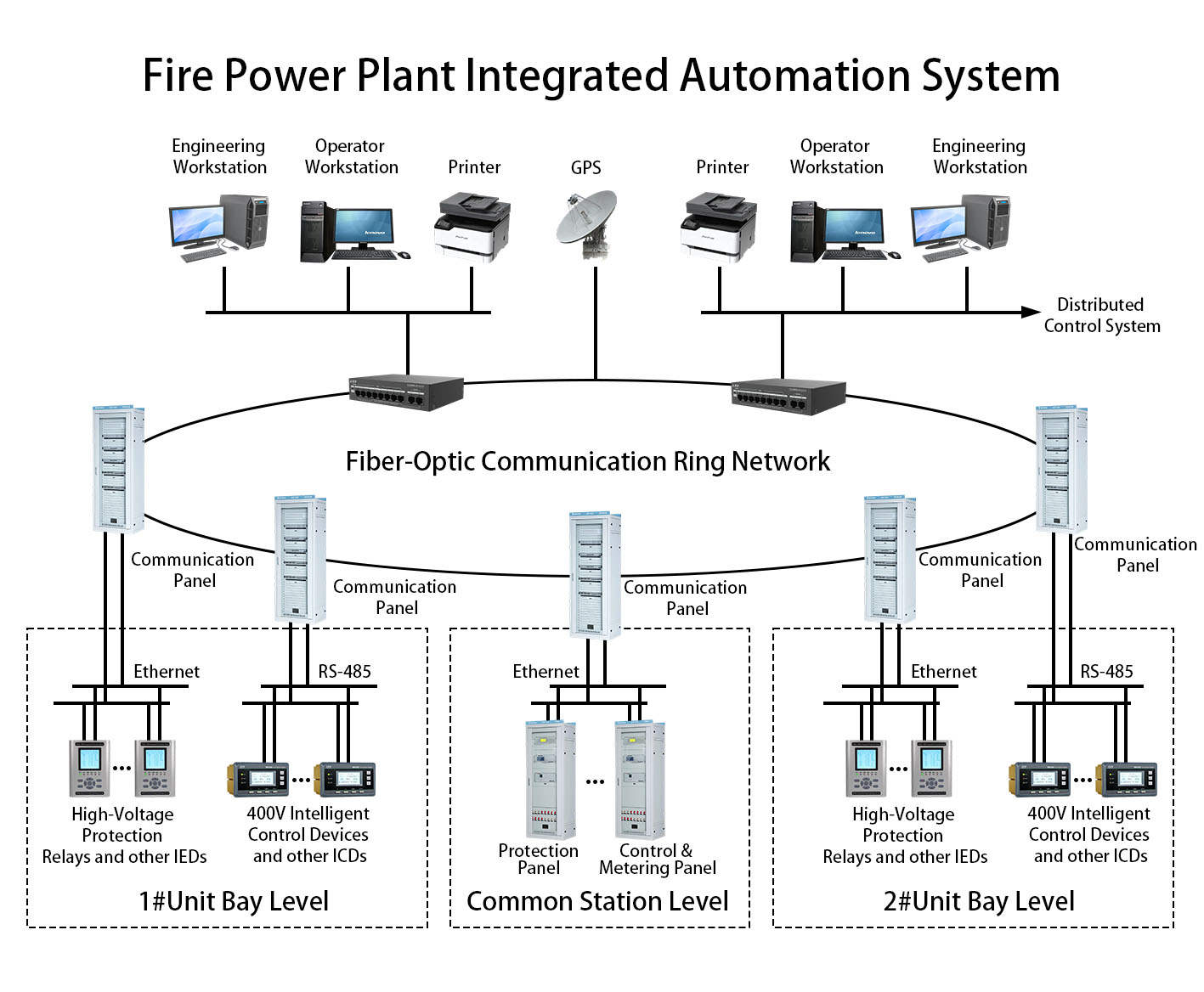
(5) Network Communication System
Utilizes industrial Ethernet, fiber-optic ring networks, or wireless communication to enable data exchange between PLCs, instruments, and SCADA workstations, with support for remote data transmission to higher-level management or cloud platforms.
(6) Security and Video Surveillance System
Includes access control systems, perimeter alarms, and CCTV cameras for plant security, visual monitoring of critical equipment, and incident recording.
(7) Energy Management System (EMS)
Incorporates power meters, energy consumption monitoring modules, and data analysis software to evaluate and optimize the efficiency of high-energy equipment (e.g., pumps, blowers), reducing operational costs.
(8) Information Management Platform
Integrates production data, equipment records, and maintenance logs, supporting big data analytics, fault diagnosis, and decision-making for intelligent operations.
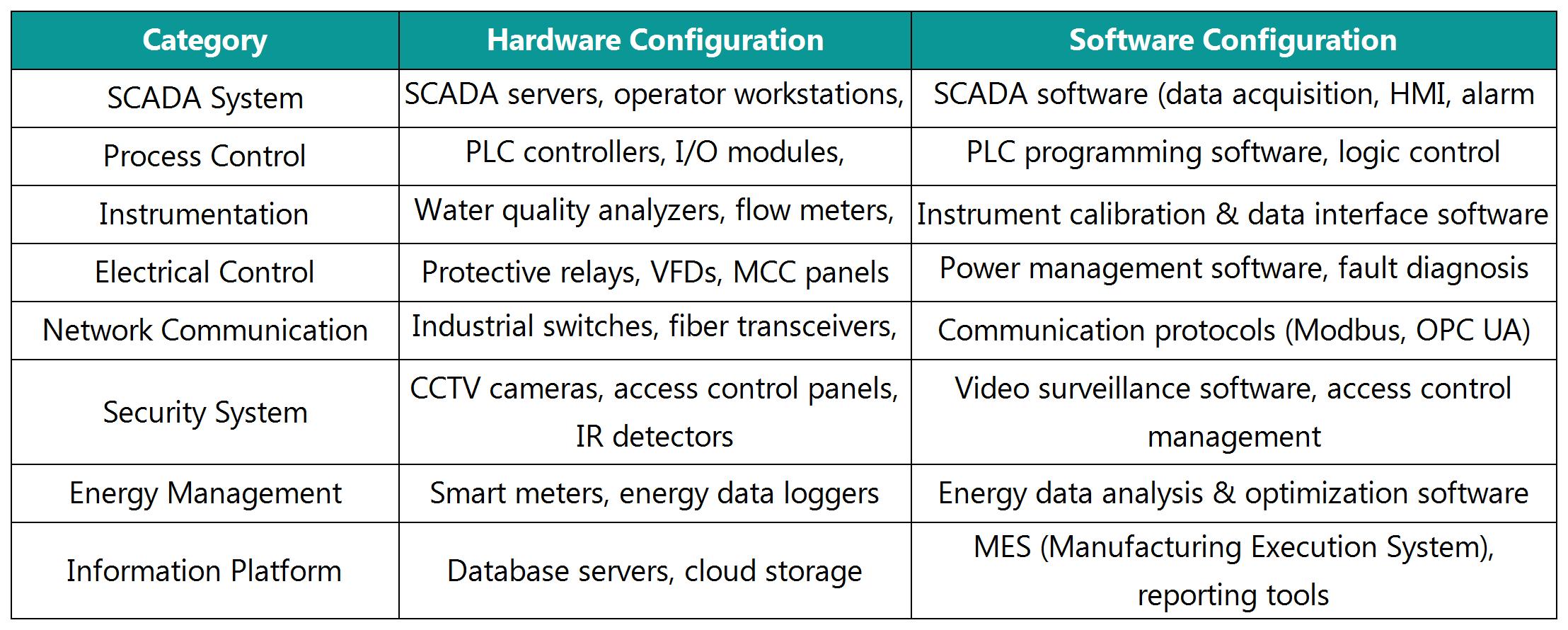
3. System Hardware and Software Configuration