1. Overview
The 33KV-11KV-0.4KV Substation Integrated Automation System is a critical component of modern power systems, enabling intelligent, digital, and networked substation management. By integrating advanced computer, communication, and electronic technologies, the system consolidates and optimizes the functions of traditional secondary substation equipment, achieving comprehensive automation in data acquisition, monitoring and control, protection relaying, energy metering, fault recording, and more.
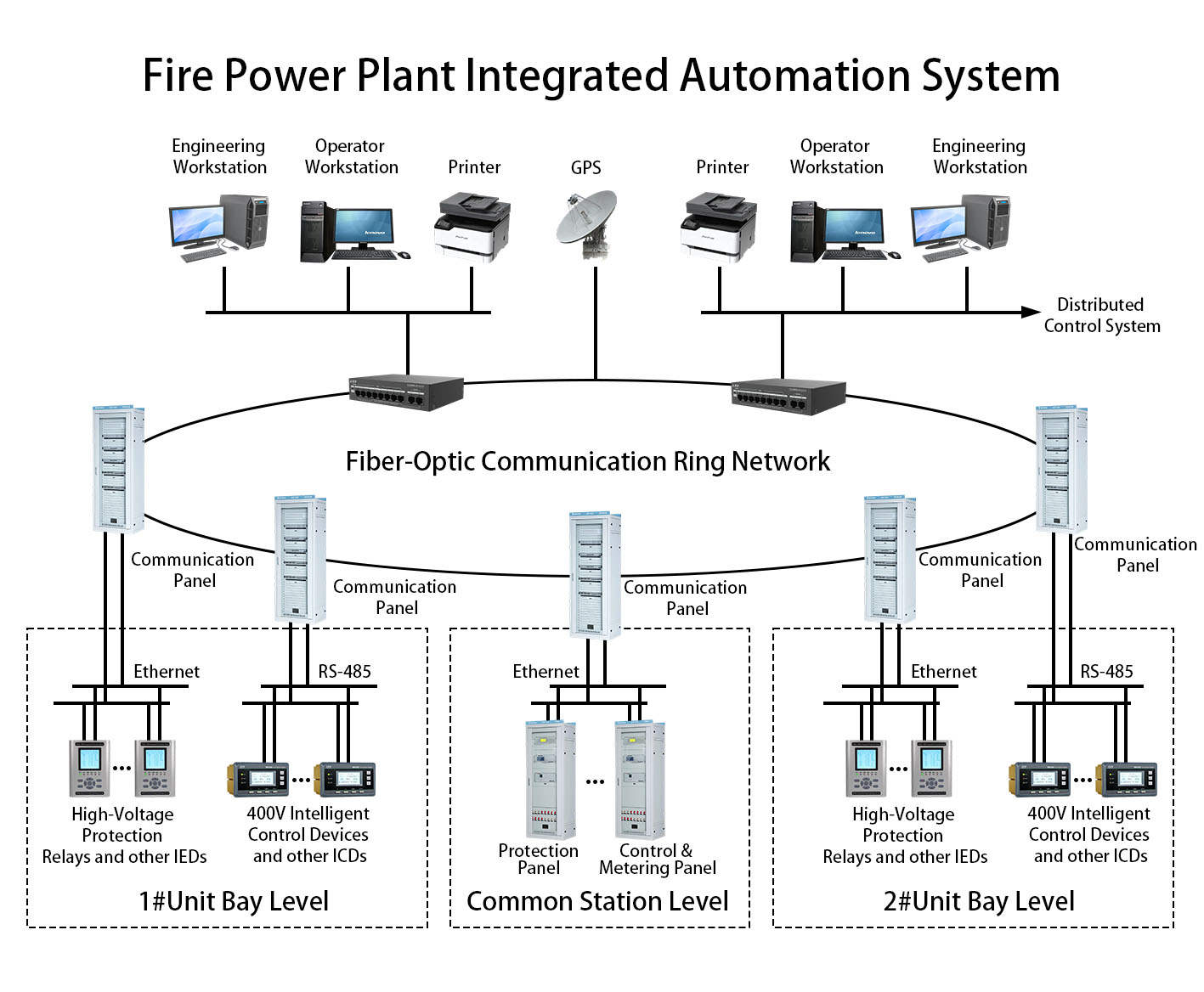
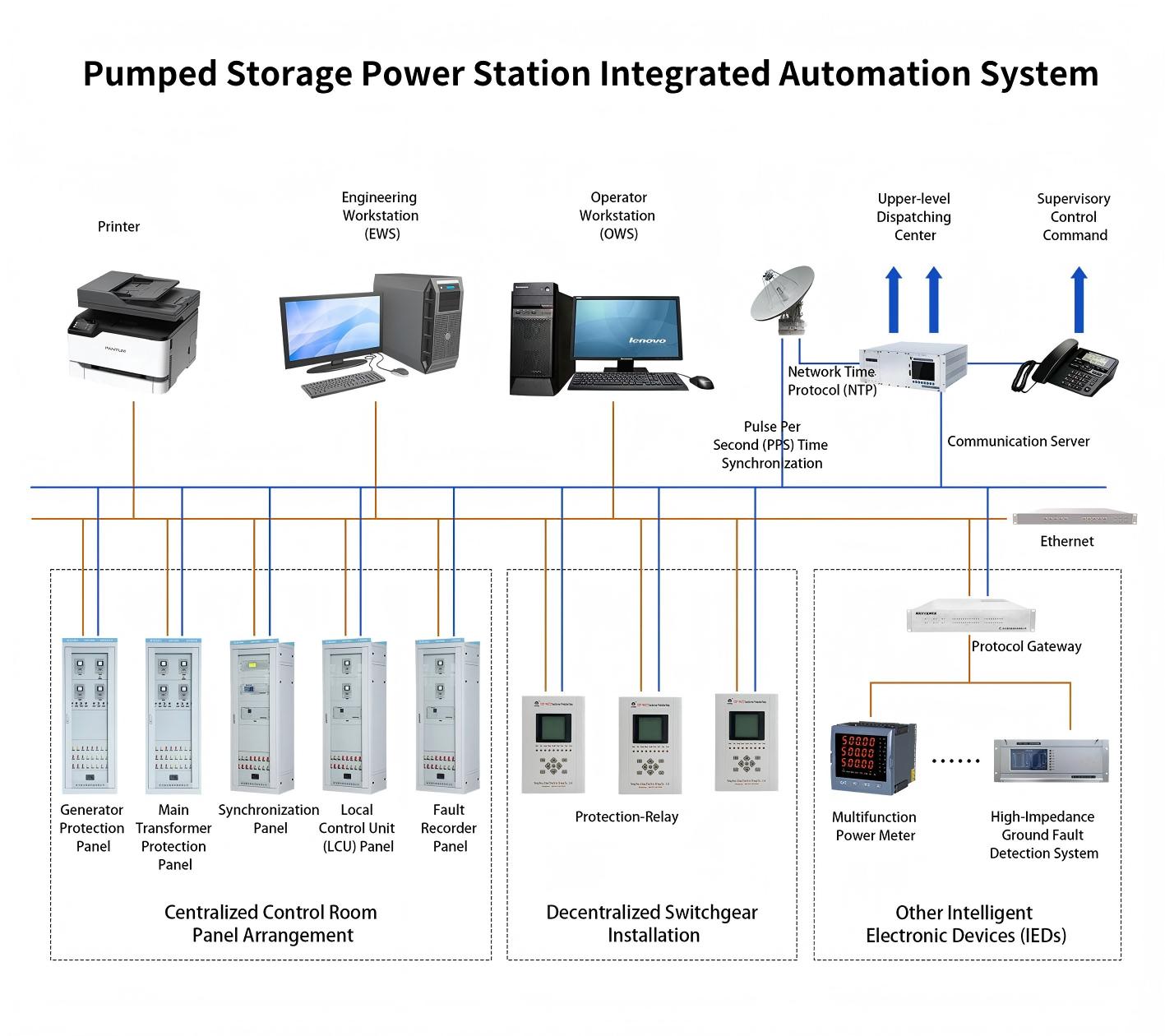
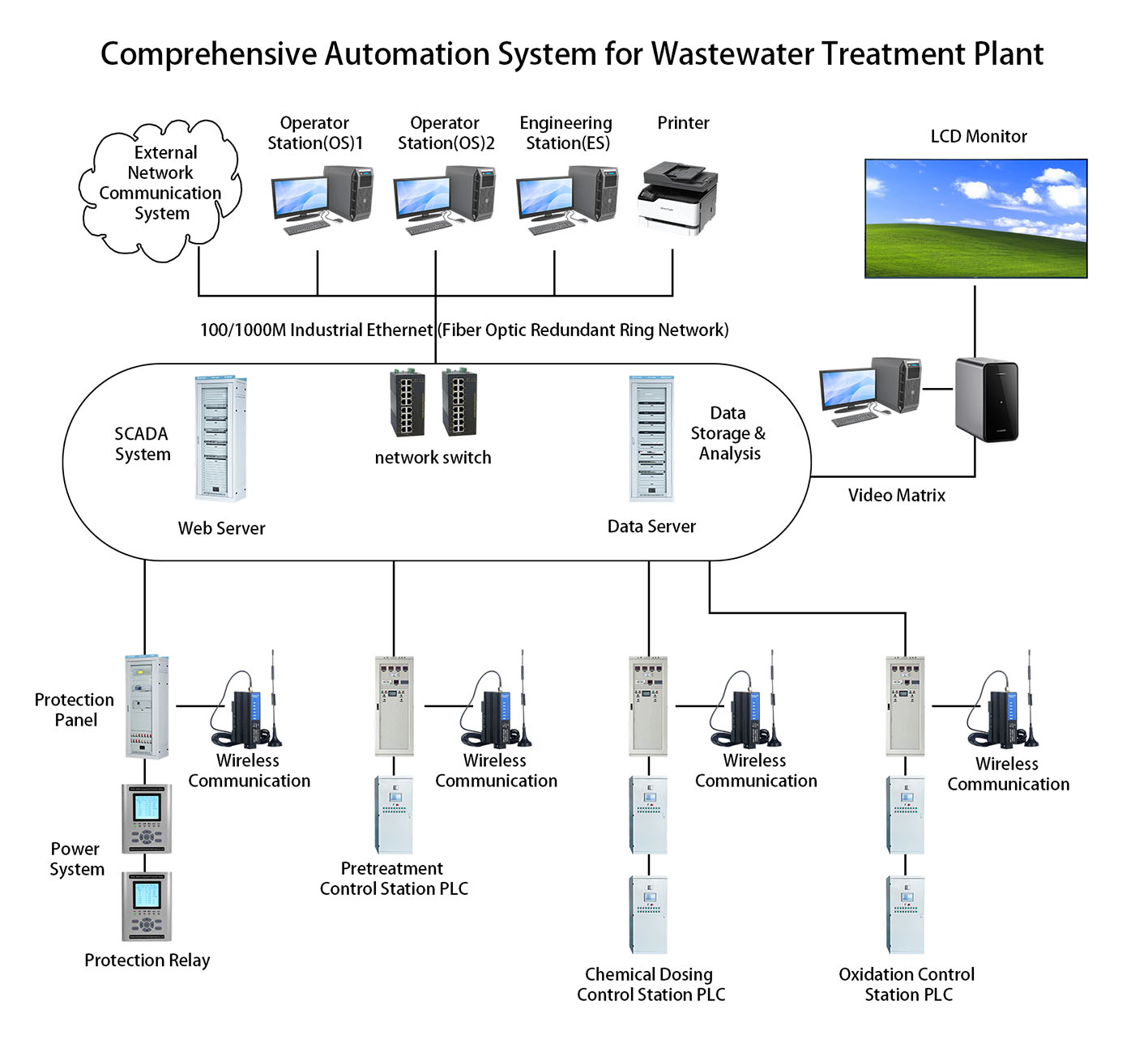
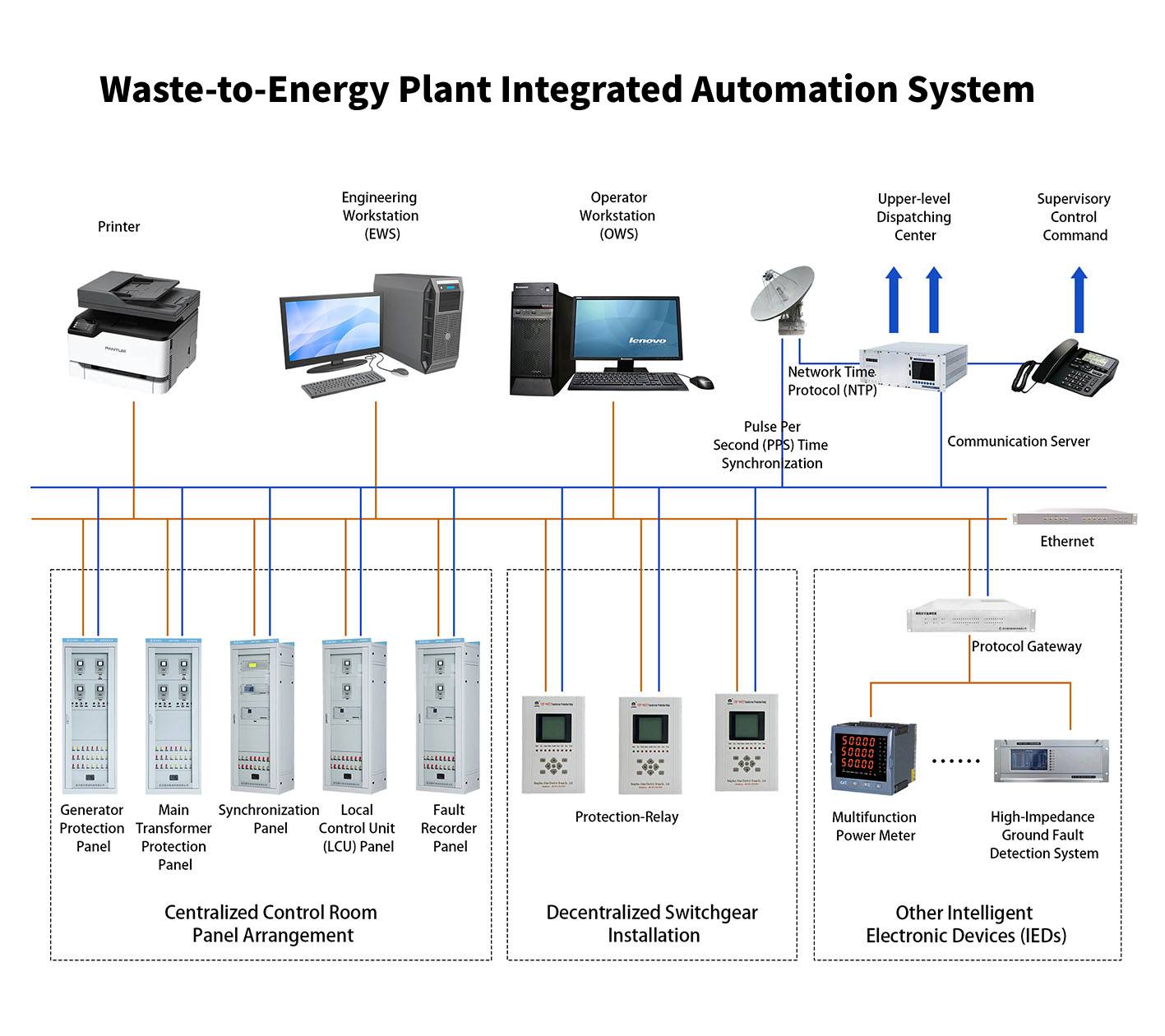
The system adopts a hierarchical and distributed architecture, consisting of station level, bay level, and process level, interconnected via high-speed communication networks. It offers high reliability, scalability, and ease of maintenance, significantly improving substation operational efficiency, reducing manual intervention, lowering operational costs, and enhancing power supply quality and reliability. This system lays a solid foundation for smart grid development.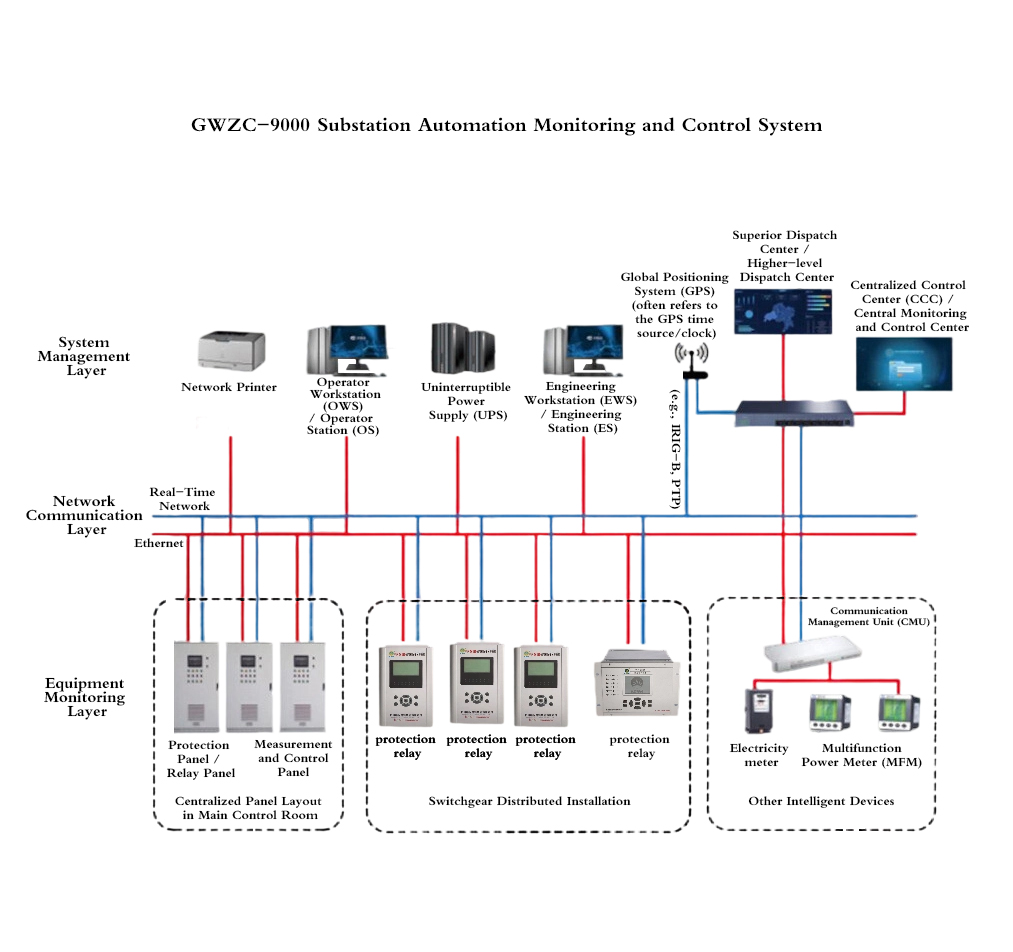 2. System Components
2. System Components
2.1 Software Section
1) SCADA System
The Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) System is the core software of the substation automation system, responsible for real-time data acquisition, processing, visualization, alarm handling, and event logging. It features a modular design, including data acquisition module, HMI (Human-Machine Interface) module, alarm processing module, and historical data storage module, supporting multiple communication protocols for seamless integration with various intelligent devices.
2) Protection Management Software
This software is used for configuring, managing, and monitoring protection relays, enabling remote setting adjustments, event logging and analysis, and real-time status monitoring of protection devices. It provides a graphical interface for operations such as protection function enabling/disabling, setting group switching, improving the efficiency and accuracy of protection management.
3) Energy Management Software
The Energy Management Software handles energy data collection, statistics, and analysis, including active/reactive energy measurement, demand calculation, and power quality monitoring. It supports multiple metering protocols (IEC 61850-9-2, DL/T 645, etc.) and interfaces with energy meters, PMUs (Phasor Measurement Units), providing data for billing and energy efficiency management.
4) Fault Diagnosis & Self-Healing System
This system employs AI-based algorithms for rapid fault location, diagnosis, and automatic restoration. By analyzing protection trip signals, fault recorder data, and SCADA real-time measurements, it enables intelligent fault identification, isolation, and fast recovery, enhancing grid resilience.
2.2 Hardware Section
1) Main Transformer Protection & Control Panel
Configuration: Includes transformer differential protection relay, backup protection relay, non-electrical protection relay (Buchholz, temperature, etc.), and measurement & control unit (MCU). Redundant configuration is applied for critical protection functions.
Function: Provides comprehensive protection for power transformers, including differential protection, overcurrent protection, zero-sequence protection, and overload protection, while performing measurement, control, and status monitoring of the transformer.
2) Feeder Protection & Control Panel
Configuration: Consists of feeder protection relay, MCU, and control switchgear, with different protection schemes for 33KV and 11KV feeders.
Function: Protects incoming/outgoing feeders with three-stage overcurrent protection, earth fault protection, and auto-reclosing, while enabling remote telemetry, telecontrol, and status indication (SCADA functions).
3) Common Measurement & Control Panel
Configuration: Includes common bay controller, communication gateway, GPS time synchronization unit, and auxiliary monitoring devices.
Function: Collects data from auxiliary systems (DC supply, station service transformer, fire protection, etc.), provides substation-wide time synchronization, and manages communication between devices.
4) Fault Recorder Panel
Configuration: Comprises digital fault recorder (DFR), data storage unit, and analysis workstation.
Function: Captures pre-fault and post-fault waveforms (voltage, current, and digital signals) for fault analysis, supporting multiple triggering modes.
5) Protection Relays (distributed in switchgear panels)
Configuration:
Feeder Protection Relays
Transformer Protection (differential, Buchholz, thermal, etc.)
Motor Protection (overload, locked rotor, unbalance, etc.)
Capacitor Bank Protection (overcurrent, overvoltage, unbalance, etc.)
Busbar Protection (differential, backup protection)
Function: Provides specialized protection for different substation equipment, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
2.3 Communication Section
1) Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) / SCADA Communication Panel
Configuration: Includes RTU, protocol converters (IEC 60870-5-101/104, DNP3.0, Modbus), and modems.
Function: Facilitates data exchange between substation and control center, transmitting telemetry, status signals, and control commands for grid monitoring and dispatch.
2) Telecontrol & Data Network Panel
Configuration: Consists of routers, Ethernet switches, encryption devices (IEC 62351 compliant), and firewalls.
Function: Establishes secure communication with the Energy Management System (EMS) via WAN (Wide Area Network), complying with cybersecurity standards (IEC 62351, NERC CIP) and supporting IEC 61850 protocols.
3. Key Features
High Reliability – Redundant design for critical protection and communication systems, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
Standard Compliance – Fully compliant with IEC 61850 (substation automation standard), ensuring interoperability.
Advanced Intelligence – Features AI-based fault diagnosis, power quality analysis, and self-healing capabilities.
Distributed Architecture – Bay-level decentralized control with high-speed Ethernet communication.
User-Friendly HMI – Intuitive graphical interface with multi-window support for efficient operation.
Cybersecurity – Implements firewalls, encryption, and access control per IEC 62351 & NERC CIP standards.
Easy Maintenance – Supports remote diagnostics, self-testing, and condition monitoring.
Energy Efficiency – Optimized for low power consumption, aligning with green substation initiatives.
This system represents state-of-the-art substation automation, delivering smart, secure, and efficient power management for modern grids.