

Applicable Scope :The GWZC-9000 Main transformer protection panel is a critical equipment in substations, power plants, and industrial distribution systems, primarily used for relay protection, monitoring, and control of power transformers. Its applicable scope includes: suitable for transformer protection at 11kV, 33kV, 69kV, 115kV, and higher voltage levels.
Product functions(ANSI):87H | 87 | 87A | 60 | 50/51 | 51 | 50N/51N | 51N | 49 | 50G/51G | 38/74 | 59 | 59N | 27 | 74 | 60 | 27/81U | 27/81L | 30 | 71G | 26/49 | 63 | 38
Communication protocols : IEC 60870-5-101/103/104 ,IEC 61850(MMS/GOOSE/SV), Modbus RTU & Modbus TCP,RJ-45 , RS-485
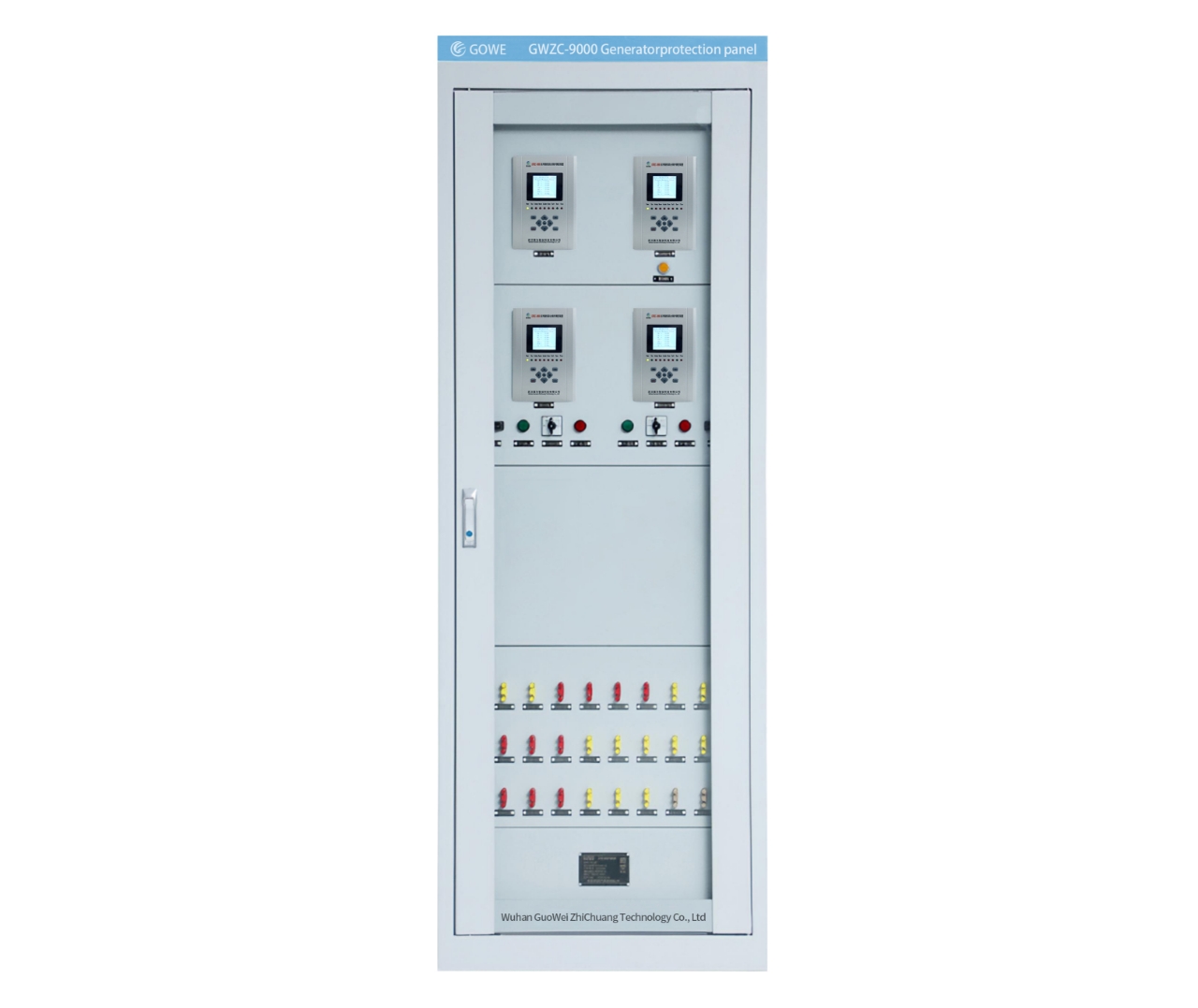
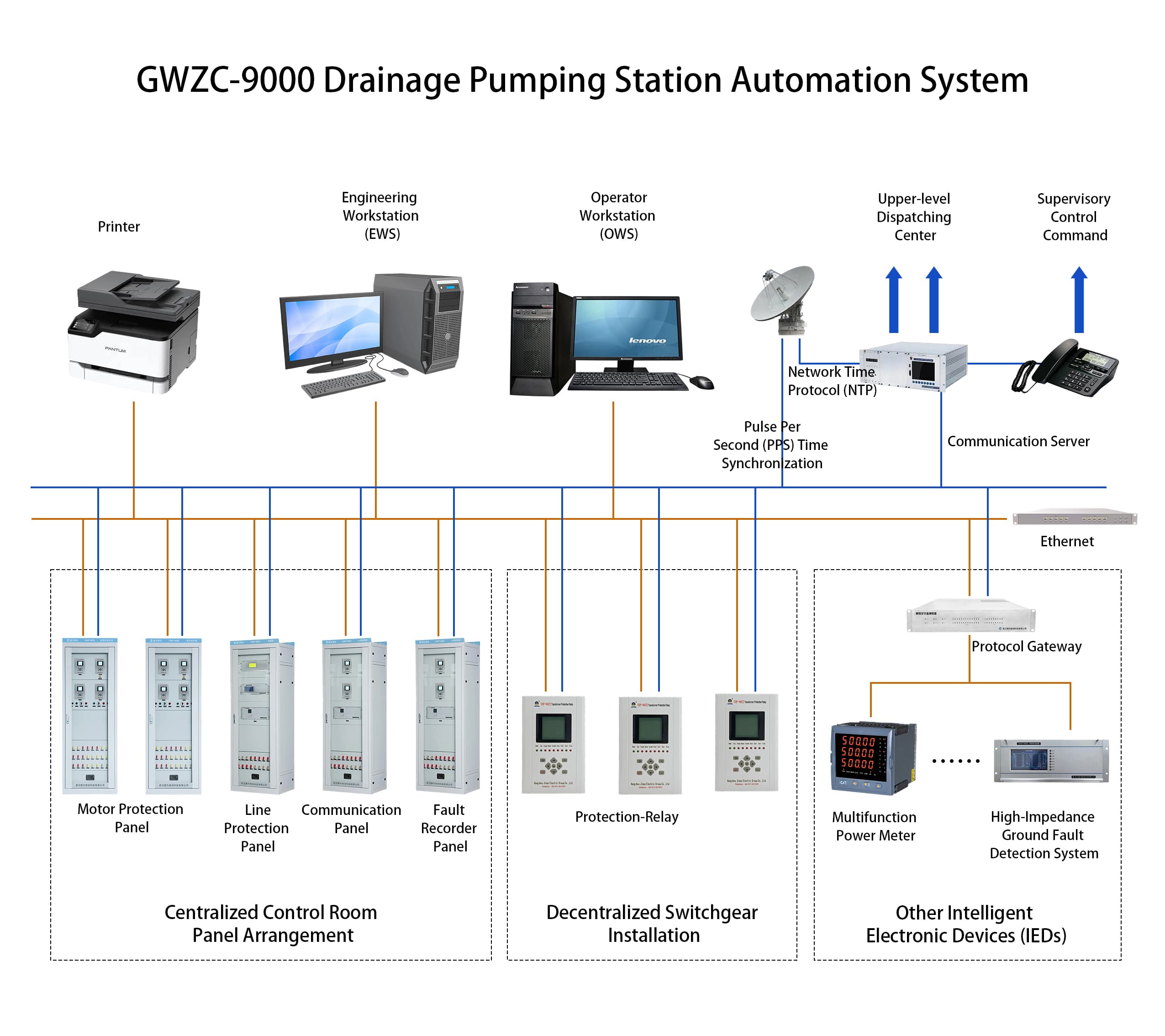
Main Transformer Protection Panel Application:
Main Transformer Protection Panel Designed for substation automation systems with voltage levels up to 132kV, 69kV, and 33kV. This integrated solution combines communication, protection, measurement, and control functions, making it the optimal choice for high-capacity main transformers.
Key Functions:
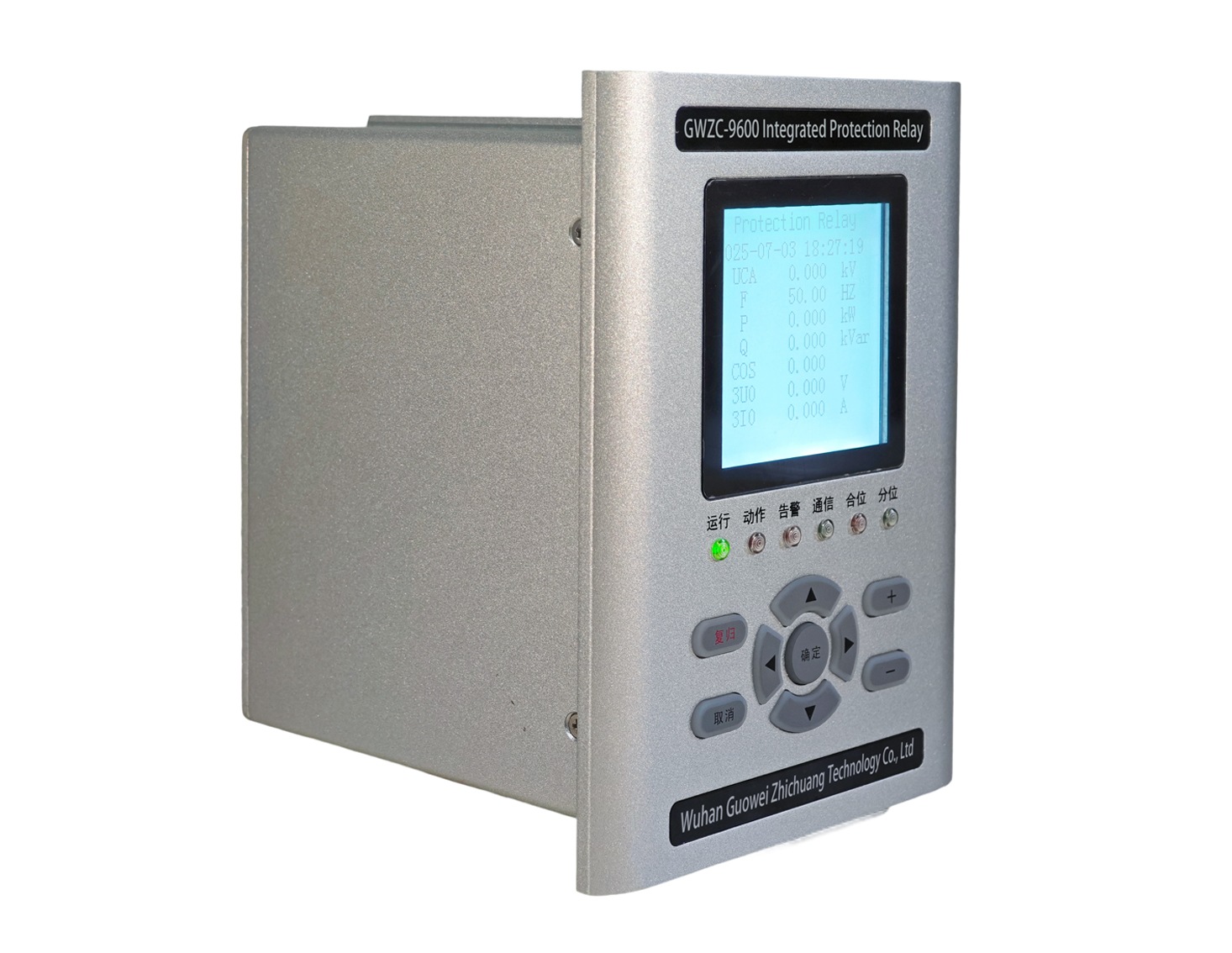
GWZC-9826 Main Transformer Differential Protection Relay
GWZC-9827 Transformer Backup Protection Relay
GWZC-9828 Transformer Non-Electrical Protection Relay
Main Transformer Measurement and Control Device
Panel and accessories
Main Transformer Protection Panel Functions (ANSI) :
GWZC-9826 Main Transformer Differential Protection Relay : Detects internal short-circuit faults (e.g., inter-turn faults) by comparing the vector sum of currents on all sides of the transformer (Kirchhoff’s current law). Features fast operation (typical operating time ≤30ms) and serves as the primary protection for transformers. (87H | 87 | 87A | 60)
GWZC-9827 Transformer Backup Protection Relay : Acts as a supplement to differential protection, addressing external faults (e.g., busbar short-circuit) or transformer overload. Includes overcurrent and zero-sequence protection (set according to IEC 60255 standards), with time-delayed operation for system coordination. (50/51 | 51 | 50N/51N | 51N | 49 | 50G/51G | 38/74 | 59 | 59N | 27 | 74 | 60 | 27/81U | 27/81L | 30)
GWZC-9828 Transformer Non-Electrical Protection Relay : Responds to non-electrical signals (e.g., Buchholz relay, oil temperature, pressure relief valve) to initiate direct tripping or alarms (e.g., light gas alarm, heavy gas trip). Complies with GB/T 14598 standards. ( 71G | 26/49 | 63 | 38)
Main Transformer Measurement and Control Device : Performs data acquisition (voltage, current, power), remote control (switching operations), and communication (IEC 61850 protocol). Supports SCADA system integration and serves as a key component in smart substations.










