

Product Overview:GWZC-9861 Bus-Tie Automatic Transfer Protection Relay is suitable for automatic transfer of incoming line switches, inner bridge switches, and main transformer switches at voltage levels below 110kV. It can be installed in panel assemblies or locally within switchgear cabinets.
Product functions(ANSI):50/51 | 51VI | 49 | 74
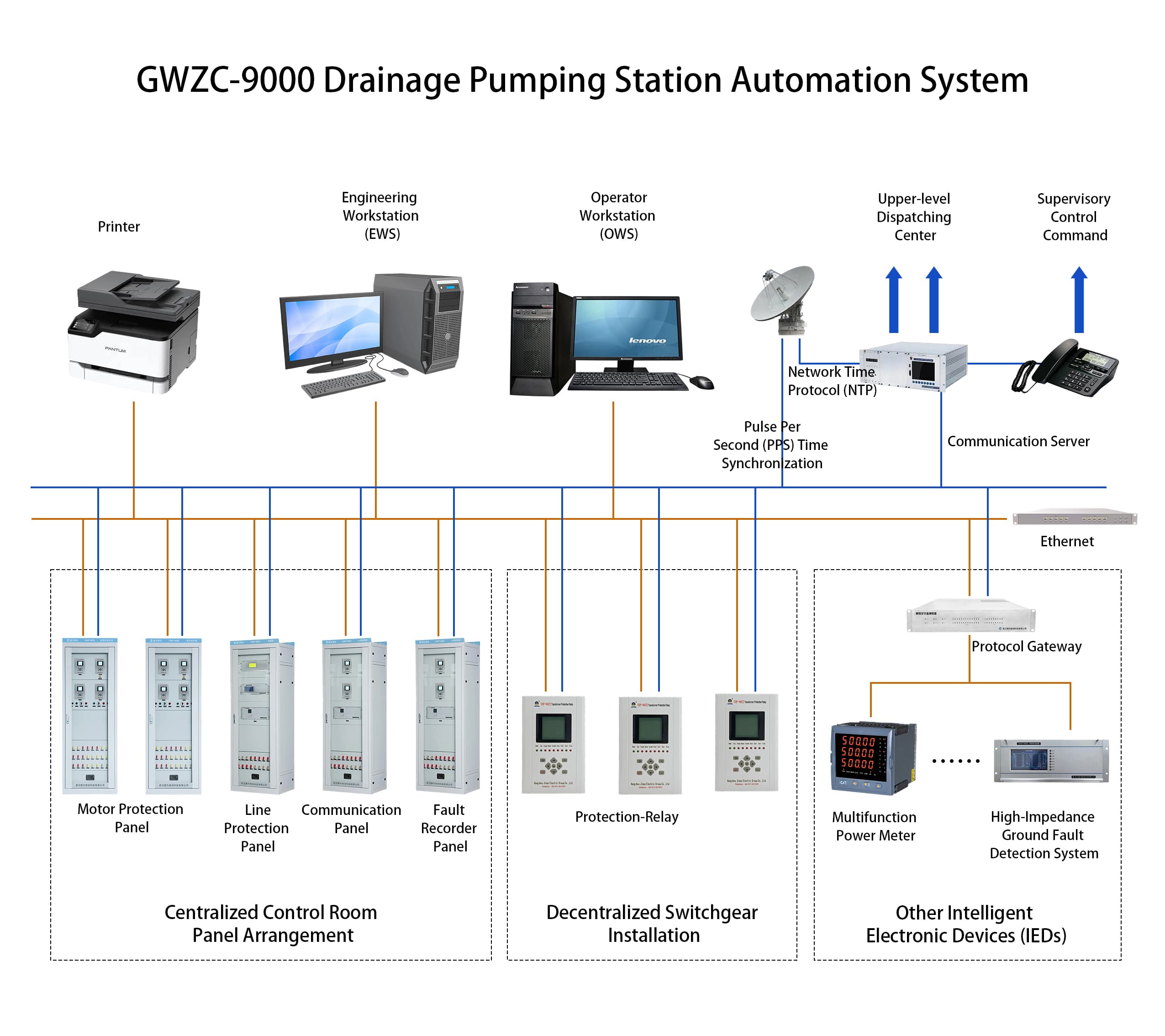
Communication functions:Supported Protocols:IEC 60870-5-103 (over Ethernet) | MODBUS RTU (via RS-485) | IEC 61850 (Ed.2 or Ed.1, as applicable)
Interfaces:2× Ethernet Ports (IEEE 802.3 compliant, 10/100 Mbps) | | 2× RS-485 Ports (ANSI/TIA-485-A standard, galvanically isolated)
Other functions: Support time synchronization via communication message, SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) time synchronization, and IRIG-B time synchronization. Support the dot matrix printing function with serial port communication. Support the fault recording function
Applicable Scope:
GWZC-9821 Bus-Tie Automatic Transfer Protection Relay is suitable for automatic transfer of incoming line switches, inner bridge switches, and main transformer switches at voltage levels below 110kV. It can be installed in panel assemblies or locally within switchgear cabinets, ensuring safe and stable operation of the power system.
Product functions(ANSI):
1.Automatic Transfer Scheme Mode 1 (Line-1 Main, Bus-Tie Closed, Line-2 Standby)
IEC 61850: ATCC (Automatic Transfer Control)
2.Automatic Transfer Scheme Mode 2 (Line-2 Main, Bus-Tie Closed, Line-1 Standby)
IEC 61850: ATCC (Automatic Transfer Control)
3.Automatic Transfer Scheme Mode 3 (Line-1 & Line-2 Split Operation, Bus-Tie Standby)
IEC 61850: ATCC (Automatic Transfer Control)
4.Automatic Transfer Scheme Mode 4 (Line-1 & Line-2 Split Operation, Bus-Tie Standby)
IEC 61850: ATCC (Automatic Transfer Control)
5.Three-Stage Overcurrent Protection | ANSI 50/51
6.Inverse Time Overcurrent Protection | ANSI 51V
7.Overload Protection | ANSI 49
8.Control Circuit Supervision | ANSI 74
Electrical Specifications
Power Supply:
● AC: 85-264V, 47-63Hz (≤15% THD)
● DC: 100-370V (≤5% ripple)
Rated AC Parameters:
● Voltage: 100V/√3 or 100V
● Current: 5A/1A
● Frequency: 50Hz
Overload Capacity:
● Current Circuit: 2×In continuous | 10×In (10s) | 40×In (1s)
● Voltage Circuit: 1.5×Un continuous
Power Consumption:
● Supply: <10W (static), ≤15W (trip)
● Current Circuit: ≤1VA/phase (5A) / ≤0.5VA/phase (1A)
● Voltage Circuit: ≤0.5VA/phase
Digital Output:
● Dry contact (8A@250VAC / 30VDC)
● Dielectric: 4kVAC (coil-contact), 1kVAC (open contact)
● Operating Time: 5ms (typ) / 8ms (max)
● Mechanical Life: 100k operations
Protection Performance
Operating Range:
● Voltage: 0.5-120V (phase)
● Current: 0.02-20×In
● Zero-Seq Current: 0.05-20A
● Frequency: 35-65Hz | Delay: 0-100s
Accuracy:
● Voltage/Current: ±2.5% or ±0.1V/±0.05A (whichever greater)
● Frequency: ±0.01Hz
● Settings: ±2.5%
Trip Time:
● Instantaneous: ≤35ms (≥1.2× setting)
● Time-Delayed: ≤1% of setting or 35ms
Measurement & Monitoring
Range:
● Voltage: 0.5-120V | Current: 0.02-1.2×In
Accuracy:
● V/I: ±0.2% | Frequency: ±0.01Hz | Other: 0.5%
● Time Sync: ≤2ms | SOE: ≤1ms
Event Recording:
● 128 protection trips/operations
● 32 self-tests/fault waveforms (COMTRADE)
Environmental & Mechanical
Operating Temp:
● Standard: -10°C to +55°C
● Extended: -40°C to +70°C*
Storage Temp: -40°C to +80°C
Humidity: 5-90% RH (non-condensing)
Pressure: 60-110 kPa
Compliance:
● IEC 60255-21 (vibration/shock)
● IEC 61000-6 (EMC)










