I. Technical Principles and Core Functions
Active Drainage Mechanism
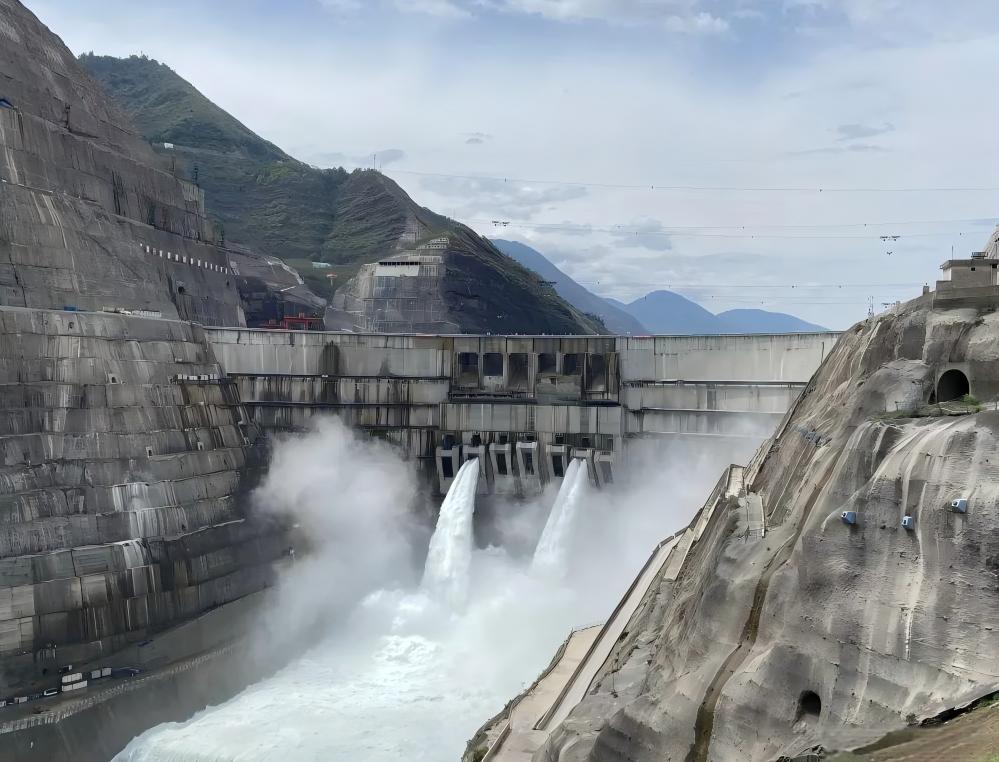
Utilizes electromechanical power (e.g., axial flow pumps, mixed flow pumps) to forcibly lift water from low-lying areas into rivers or drainage networks, overcoming the limitations of natural gravity drainage. For example, during the 2023 Guangdong rainstorm, the Huangpu Pump Station in Guangzhou drained 1.2 million cubic meters of water in a single day—equivalent to 860 standard swimming pools.
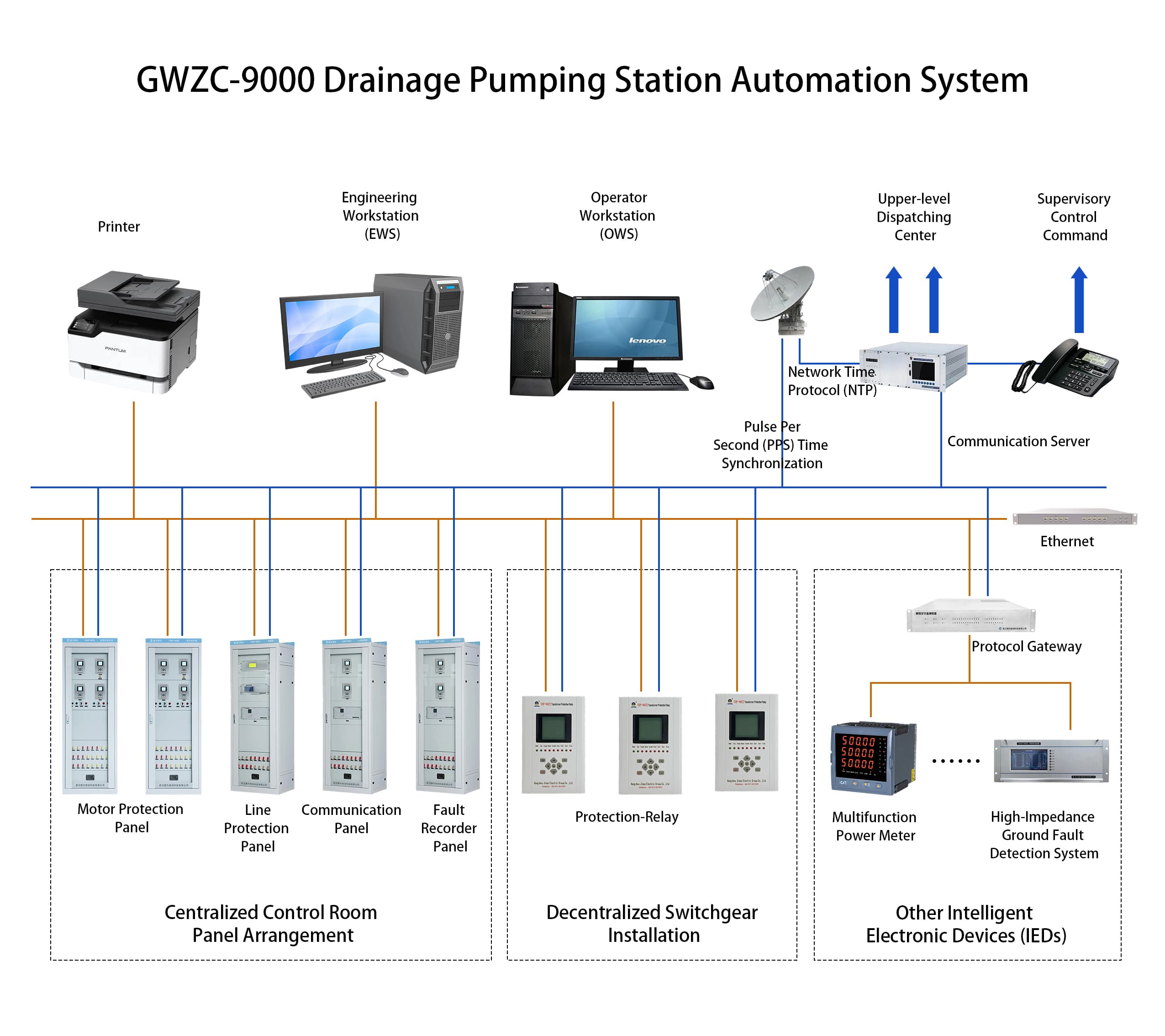
Intelligent Control System
Modern pump stations integrate IoT sensors and AI algorithms to monitor water levels (with ±1cm accuracy), rainfall, and pipe network load in real time, automatically adjusting unit operations. For instance, the Suzhou Creek Pump Station Group in Shanghai reduced urban floodwater drainage time by 40% through its smart dispatch platform.
Emergency Backup Power
Equipped with diesel generators or energy storage systems to ensure continuous operation during power outages. During the catastrophic “7·20” rainstorm in Zhengzhou (2021), pump stations with dual power sources improved disaster mitigation efficiency by 300%.
II. Smart Monitoring and Early Warning System
Distributed IoT Monitoring Network
Deploys low-cost water level sensors (ultrasonic/pressure-based), rain gauges, and soil moisture probes to create an urban-rural 3D monitoring network.
Case Study: Huawei and the Ministry of Water Resources’ “Smart Water Conservancy” project installed 5,000+ monitoring points in the Pearl River Delta, reducing warning response time to 15 minutes.
AI Flood Prediction Model
Combines weather radar, GIS terrain data, and historical disaster databases to develop LSTM neural network prediction models.
Technical Indicators: Achieves <10% error in 6-hour runoff forecasts and 85% accuracy in submerged area predictions.
Emergency Communication Relay System
Develops flood-resistant Mesh ad-hoc network devices to maintain communication during base station failures (MIIT test standard: 72-hour continuous operation).
III. Digital Twin Platform
3D Visualization Decision System
Asset Health Management
Disaster Damage Assessment AI
IV. Socio-Economic Value Quantification
Direct Disaster Mitigation Benefits
Ecological Synergy Effects