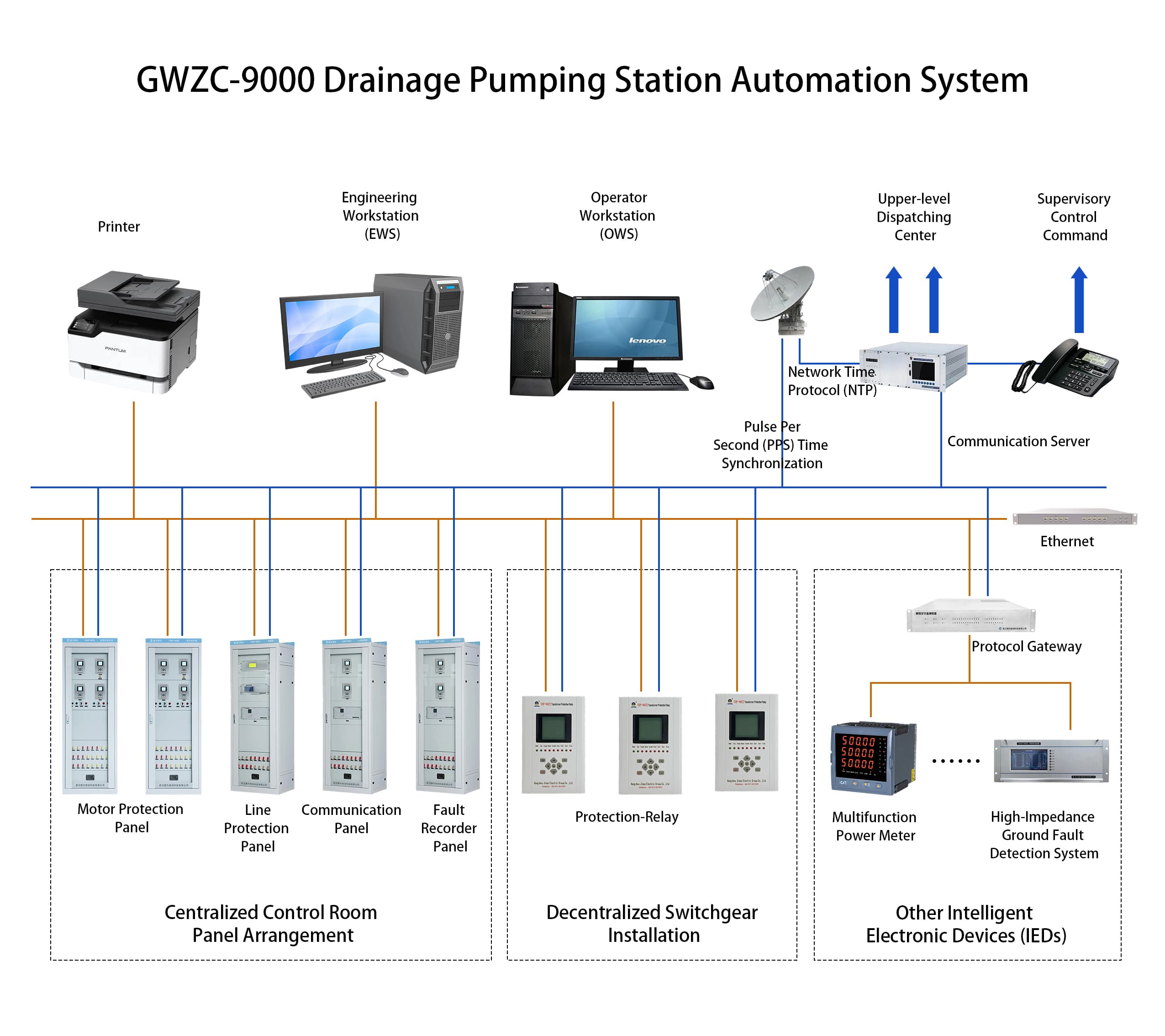
I. Basic Information on Standard Publication
1.Standard Names & Numbers:
IEC 63522-6:2025 Electrical Relays – Tests and Measurements – Part 6: Contact Circuit Resistance (or Voltage Drop)
IEC 63522-35:2025 Electrical Relays – Tests and Measurements – Part 35: Resistance to Cleaning Agents
IEC 63522-36:2025 Electrical Relays – Tests and Measurements – Part 36: Fire Hazard
2.Issuing Body: International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
3.Leading Organization: Xiamen Hongfa Electroacoustic Co., Ltd. (China) (World’s largest relay manufacturer, ranked first globally in market share for consecutive years)
4.Release Date: February 2025 (Parts -6 and -36) / May 2025 (Part -35)
II. Technical Specifications of the Three Core Standards
1. IEC 63522-6:2025: Contact Circuit Resistance (or Voltage Drop)
Scope: Standardizes test methods for circuit resistance or voltage drop of relay contacts in the closed state.
Key Requirements:
Verify that contact resistance remains within specified limits to ensure long-term conductive stability;
Quantify resistance changes caused by contact oxidation/wear to prevent circuit failure.
Test Method: Apply rated current via a constant current source; measure voltage drop across contacts and calculate resistance.
2. IEC 63522-35:2025: Resistance to Cleaning Agents
Scope: Tests corrosion resistance of relays exposed to industrial chemical cleaning agents.
Key Requirements:
Simulate material tolerance after exposure to cleaning agents (e.g., solvents, acids/alkalis) during manufacturing or maintenance;
Evaluate impacts of seal aging and metal contact corrosion on product lifespan.
Test Method: Accelerated aging tests; record material deformation and electrical performance degradation.
3. IEC 63522-36:2025: Fire Hazard Assessment
Scope: Fire safety performance of relays under abnormal operating conditions.
Key Requirements:
Ensure relays do not ignite during overload/short-circuit, or that flames self-extinguish within defined time/range;
Restrict use of flammable materials to mitigate fire risks.
Test Method: Apply fault current; monitor temperature rise, smoke emission, and ignition; record flame duration.
Table: Key Technical Parameters and Test Objectives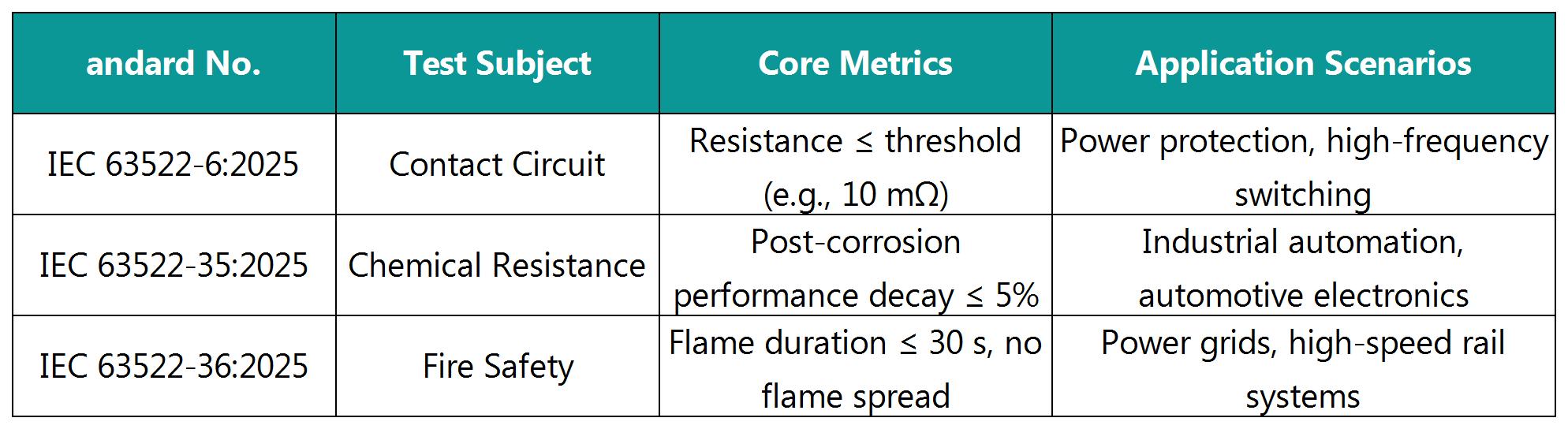
III. Standard Development Background & Process
1.Technical Drivers:
Previous IEC standards (2006) lagged behind reliability/safety requirements for relays in emerging fields (e.g., renewable energy, smart grids);
Global absence of unified corrosion/fire safety test protocols caused product quality inconsistencies.
2.China’s Leading Role:
Xiamen Hongfa convened multinational experts, proposing test protocols based on its global engineering expertise (>50% market share);
Validated methodology via experimental data (e.g., accelerated aging datasets) after >20 technical debates.
3.Timeline & Challenges: Finalized after 3 years; key disputes (e.g., fire-test current thresholds, cleaning agent concentration) resolved with Chinese proposals as baseline.
IV. Significance of Standard Publication
1.Technical Advancement:
Establishes unified global test benchmarks, reducing trade barriers from standard disparities;
Drives relays toward higher reliability/longevity (e.g., 100,000-operation lifespan for EV relays).
2.Industrial Competitiveness:
Elevates China from “manufacturing hub” to “standard-setting leader”, enhancing global pricing power;
Benefits Xiamen relay industrial cluster (5 manufacturers + 21 upstream/downstream firms) via technical spillover.
3.Safety & Sustainability:
Reduces fire risks in critical infrastructure (e.g., high-speed rail power networks);
Minimizes industrial e-waste through corrosion-resistance standards.
V. Industry Impact & Future Outlook
Short Term: Mandatory compliance in regions (e.g., EU); Chinese testing bodies gain first-mover advantage.
Long Term: China plans standards for intelligent, low-power relays, synchronizing domestic/international development.
Challenge: SMEs face cost pressures from production-line upgrades (e.g., fire-resistant materials).
Note: Terminology strictly adheres to IEC norms, e.g., “Contact Circuit Resistance,” “Fire Hazard.” Refer to IEC 63522 series for original text.